NIST Updates Database Used for Designing Advanced Materials
The Phase Equilibria Diagrams Database accelerates development of new materials across a wide range of critical U.S. industries.
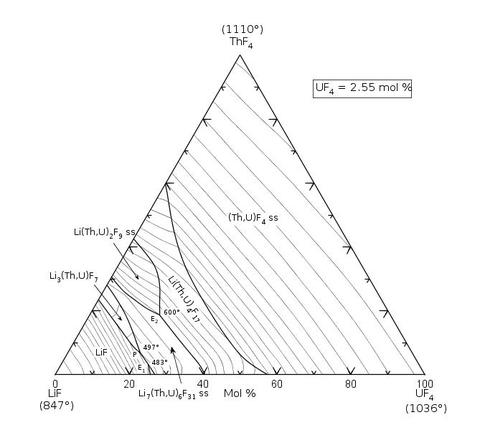
A phase diagram from Standard Reference Database 31 including Lithium, Thorium, and Uranium. Newly added diagrams assist researchers with challenges in emerging energy technologies.
No one can say with absolute certainty what will happen in the future. But scientists can predict the future state of advanced materials very precisely using NIST’s Standard Reference Database (SRD) 31, also known as the Phase Equilibria Diagrams Database.
Now, NIST has released SRD 31 version 4.5, an update that includes 268 new entries and 720 new diagrams describing combinations of materials, including many new systems that may be key to solving the nation’s energy and climate challenges.
Phase equilibria diagrams show the state — solid, liquid or gas — that a mixture of materials will ultimately reach at a given temperature and pressure. Knowing this information in advance accelerates the development of new materials.
“When you start designing a new material, you need to know what will happen to it under different conditions,” said Igor Levin, the NIST materials scientist who oversees SRD 31. “This database helps researchers home in much more quickly on the combinations of materials that will have the precise properties they seek.”
Researchers rely on SRD 31 to develop new materials — and improve existing ones — for countless applications, including semiconductors, solar cells, chemical sensors, video displays, data storage and dental restoration materials, to name just a few.
The diagrams included in the new update will help researchers address challenges in emerging energy technologies, including corrosion issues in molten-salt generation IV nuclear reactors, heat transfer and storage in nuclear and concentrated solar power facilities, and development of next-generation batteries.
The new update can also help in developing new processes for recycling rare earth minerals and in reducing carbon emissions from metallurgical processing.
NIST scientists create content for the database by scouring newly published research literature for phase-diagram studies. Subject-matter experts at NIST and elsewhere standardize the phase diagrams to meet NIST guidelines and provide critical commentaries. NIST scientists provide quality control at each step in the process.
The Phase Equilibria Diagrams Database contains more than 30,000 diagrams for inorganic systems. Materials covered include oxides and nonoxide systems such as chalcogenides and pnictides, phosphates, salt systems and mixed systems of these classes.
The companion PED Editor for digitizing phase diagrams and extracting data from phase diagrams or other two‐dimensional scientific drawings is available for free download.
SRD 31 Version 4.5 is available for purchase as a PC product and also online as a subscription.
A free demonstration version of SRD 31 is available that displays the full functionality of the application and includes a searchable index of all materials systems covered in the database, including the new materials added in this release.

