Summary
Absorbed dose is the energy imparted per unit mass by radiation to an irradiated target. The SI unit of absorbed dose is the gray (abbreviated Gy), equivalent to J/kg, and it is realized most directly via calorimetry. In the US, calibrations of dosimetry instrumentation used in industry and medicine are traceable to a NIST water calorimeter irradiated in Co-60 gamma rays. To meet existing and anticipated calibration needs, NIST is developing water calorimeters for use in other beam qualities.
Description
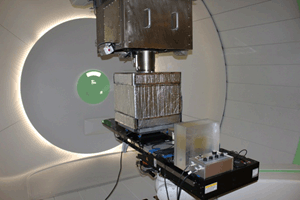
While NIST maintains the original standard for use in Co-60, preliminary work has been done to commission a standard for use in high-energy x-ray beams from the NIST medical linear accelerator (Varian Clinac 2100C). Completion of this task will enable NIST to provide direct calibrations in 6 MV and 18 MV x-rays used routinely in radiotherapy. Similar work toward commissioning a standard for high-energy electron beams, used less frequently in radiotherapy, is also underway for 6 MeV to 20 MeV beams from the same Clinac 2100C.
As radiotherapy with proton beams becomes a standard of care for many types of cancer, protocols and standards for proton-beam dosimetry will become necessary. No international consensus yet exists defining standard reference conditions for dosimetry of radiotherapy proton beams, however several national metrology institutes (NMIs), including NIST, have developed or are developing water calorimeters to fill the eventual need. Because NIST has no proton accelerator, preliminary work has been done off-site, at the Hampton University Proton Therapy Institute (Hampton, VA) and at the M.D. Anderson Proton Therapy Center (Houston, TX), both involving double-scattered proton beams used for treating cancer patients. Future work to ruggedize the instrument for such travel will prepare NIST for remote transferring of standards.
Dose standards for radiotherapy-level medium-energy x-ray beams, in the range of 100 kV to 300 kV, have also become a priority for the international community, and NIST is developing a water calorimeter for use with such beams. Because of the much shallower depth-dose profile in water at those energies, a modified vessel and phantom are needed. The instrument requirements are also expected to be advantageous for calorimetry of 6 MV electron beams, thus a standard calorimeter appropriate for both types of beams may emerge from this work.

