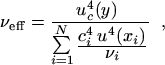NIST TN 1297: Appendix B. Coverage Factors
B.1 This appendix summarizes a conventional procedure, given by the Guide [2] and Dietrich [10], intended for use in calculating a coverage factor k when the conditions of the Central Limit Theorem are met (see subsection 5.4) and (1) a value other than k = 2 is required for a specific application dictated by an established and documented requirement; and (2) that value of k must provide an interval having a level of confidence close to a specified value. More specifically, it is intended to yield a coverage factor kp that produces an expanded uncertainty Up = kpuc(y) that defines an interval y - Up ≤ Y ≤ y + Up, which is commonly written as Y = y ± Up, having an approximate level of confidence p.
The four-step procedure is included in these guidelines because it is expected to find broad acceptance internationally, due in part to its computational convenience, in much the same way that k = 2 has become the conventional coverage factor. However, although the procedure is based on a proven approximation, it should not be interpreted as being rigourous because the approximation is extrapolated to situations where its applicability has yet to be fully investigated.
B.2 To estimate the value of such a coverage factor requires taking into account the uncertainty of uc(y), that is, how well uc(y) estimates the standard deviation associated with the measurement result. For an estimate of the standard deviation of a normal distribution, the degrees of freedom of the estimate, which depends on the size of the sample on which the estimate is based, is a measure of its uncertainty. For a combined standard uncertainty uc(y), the "effective degrees of freedom" νeff of uc(y), which is approximated by appropriately combining the degrees of freedom of its components, is a measure of its uncertainty. Hence νeff is a key factor in determining kp. For example, if νeff is less than about 11, simply assuming that the uncertainty of uc(y), is negligible and taking k = 2 may be inadequate if an expanded uncertainty U = kuc(y) that defines an interval having a level of confidence close to 95 percent is required for a specific application. More specifically, according to Table B.1 (to be discussed below), if νeff = 8, k95 = 2.3 rather than 2.0. In this case, and in other similar cases where νeff of uc(y) is comparatively small and an interval having a level of confidence close to a specified level is required, it is unlikely that the uncertainty of uc(y) would be considered negligible. Instead, the small value of νeff, and thus the uncertainty of uc(y), would probably be taken into account when determining kp.
B.3 The four-step procedure for calculating kp is as follows:
1) Obtain y and uc(y) as indicated in Appendix A.
2) Estimate the effective degrees of freedom νeff of uc(y) from the Welch-Satterthwaite formula
where ci ≡ ∂f/∂xi, all of the u(xi), are mutually statistically independent, νi is the degrees of freedom of u(xi), and
The degrees of freedom of a standard uncertainty u(xi) obtained from a Type A evaluation is determined by appropriate statistical methods [7]. In the common case discussed in subsection A.4 where
$$x_i = \bar{X}_i$$
and
$$u(x_i) = s(\bar{X}_i),$$
the degrees of freedom of u(xi) is νi = n - 1. If m parameters are estimated by fitting a curve to n data points by the method of least squares, the degrees of freedom of the standard uncertainty of each parameter is n - m.
The degrees of freedom to associate with a standard uncertainty u(xi) obtained from a Type B evaluation is more problematic. However, it is common practice to carry out such evaluations in a manner that ensures that an underestimation is avoided. For example, when lower and upper limits a- and a+ are set as in the case discussed in subsection A.5, they are usually chosen in such a way that the probability of the quantity in question lying outside these limits is in fact extremely small. Under the assumption that this practice is followed, the degrees of freedom of u(xi) may be taken to be νi → ∞.
NOTE - See the Guide [2] for a possible way to estimate νi when this assumption is not justified.
3) Obtain the t-factor tp(νeff) for the required level of confidence p from a table of values of tp(ν) from the t-distribution, such as Table B.1 of this Appendix. If νeff is not an integer, which will usually be the case, either interpolate or truncate νeff to the next lower integer.
4) Take kp = tp(νeff) and calculate Up = kpuc(y).
Contacts
-
PML webmaster