New Collaboration Aims to Improve Measurement of Viral Vectors Used in Cutting-Edge Gene Therapies
A large interlaboratory study of adeno-associated virus (AAV), an important tool in gene therapy, will be led by USP and NIST in collaboration with NIIMBL.
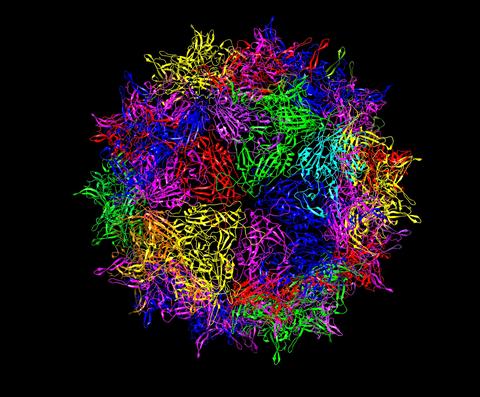
A ribbon diagram showing a portion of the protein shell of an adeno-associated virus used for delivering gene therapies. The colored ribbons represent different proteins.
ROCKVILLE, Md. — The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the National Institute for Innovation in Manufacturing Biopharmaceuticals (NIIMBL) and United States Pharmacopeia (USP) have announced a research collaboration to assess analytical methods and develop standards for adeno-associated virus (AAV), an important mechanism for delivering gene therapies.
AAVs are particularly useful for gene therapies because they are not known to cause human disease and cannot replicate on their own. AAV-based therapies are currently used to treat a type of inherited retinal dystrophy that causes blindness and spinal muscular atrophy in children, and treatments for many more diseases are currently being developed. However, to use AAVs most effectively, scientists need to accurately measure attributes related to their quality. These attributes include the purity of the AAV product and the relative number of virus particles that contain the full genetic payload.
At a workshop hosted by NIIMBL in 2019, academic and industry scientists, product developers, instrument manufacturers and other stakeholders identified needs for improved consistency of measurement methods and physical standards for AAV-based products as top priorities.
“AAV is important because these are critical components to manufacture a variety of gene and cell therapy products,” explained Kelvin Lee, NIIMBL institute director. “By addressing the quality attributes assessment of viral vectors, the field of gene therapies as a whole will benefit from access to high quality components to enable the development of a variety of products.”
As part of this collaboration, USP and NIST will conduct an interlaboratory study in which multiple laboratories will measure these critical quality attributes and their results will be compared and analyzed. This will contribute to the standardization of measurement methods and the development of physical reference materials that will improve measurement consistency across the industry. The study will take two to three years to complete.
“There is great level of synergy between the organizations engaged in this collaboration,” said Fouad Atouf, USP vice president of global biologics. “NIST’s long-standing experience with measurement sciences and USP’s established role in the application of measurement to the development of methods and associated reference standards is a great combination to advance the field of testing of biopharmaceuticals. NIIMBL provides the appropriate collaborative platform and access to the right stakeholders.”
“This work will help build trust in the quality of AAV,” said NIST research scientist and chemical engineer Wyatt N. Vreeland, who will be leading the NIST component of the collaboration. “And it will support the development of promising new gene therapies that will greatly improve peoples’ lives.”
About NIST
The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) promotes U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life. NIST supports the biomanufacturing sector by improving measurement science for the accurate and reproducible characterization of a wide range of processes and products and through the development of reference materials and interlaboratory comparisons.
About NIIMBL
The National Institute for Innovation in Manufacturing Biopharmaceuticals (NIIMBL) is a public-private partnership whose mission is to accelerate biopharmaceutical innovation, support the development of standards that enable more efficient and rapid manufacturing capabilities, and educate and train a world-leading biopharmaceutical manufacturing workforce, fundamentally advancing U.S. competitiveness in this industry. NIIMBL is part of Manufacturing USA®, a diverse network of federally sponsored manufacturing innovation institutes, and is funded through a cooperative agreement with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the U.S. Department of Commerce with significant additional support from its members.
About USP
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) is an independent scientific organization that collaborates with the world’s top experts in health and science to develop quality standards for medicines, dietary supplements and food ingredients. USP’s standards are used in the U.S. and other countries to ensure the quality of thousands of products including cardiovascular, oncology, endocrine and antibiotic drugs. Through its standards, advocacy and education, USP helps increase the availability of quality medicines, supplements and food for billions of people worldwide.
Media Contacts
NIST
Richard Press
richard.press [at] nist.gov (richard[dot]press[at]nist[dot]gov)
NIIMBL
Maria Chacon
mchacon [at] udel.edu (mchacon[at]udel[dot]edu)
USP
Anne Bell
ADB [at] USP.org (ADB[at]USP[dot]org)

