Summary
We live in a network-centric society that increasingly relies on the Internet’s routing infrastructure to facilitate human communication, connect users to online services, interconnect distinct components of modern cloud computing systems, and enable devices to interact in the Internet of Things (IoT).
As originally designed, the Internet’s routing infrastructure has systemic vulnerabilities that expose many critical systems to theft of service, loss of privacy, and wide-scale outages. NIST is working with industry to design, standardize, and foster deployment of technologies to improve the security and resilience of Internet Routing
Description

Today’s global Internet is comprised of roughly 1,000,000 distinct destination routes interconnected by 60,000 enterprise and Internet Service Provider (ISP) networks. The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the “glue” that enables the modern Internet, by exchanging reachability information about each destination among interconnected ISPs. Each autonomous network uses BGP data, along with its own business policies, to compute the paths which user data will follow.
As currently deployed, BGP lacks the ability to authorize, authenticate, or protect the integrity of these global information exchanges or means to detect and mitigate large-scale policy violations [1]. The result is ever-increasing occurrences of “BGP Hijacks” in which malicious parties falsely claim reachability to destinations to steal their traffic, or forge information about their paths to detour traffic along routes that facilitate other attacks on the communicating systems and the information they exchange.
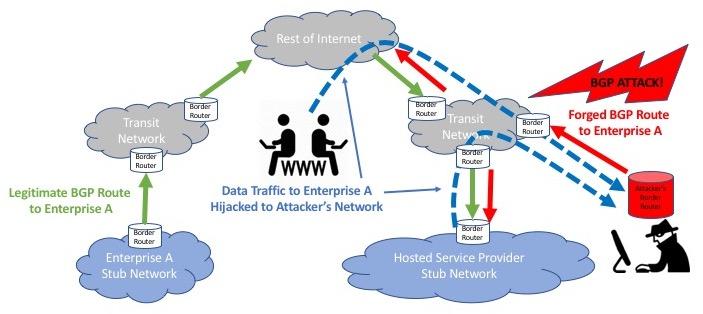
In addition to malicious hijacks, common configuration errors often result in large-scale “BGP leaks” in which routing information is exchanged in violation of contracted business policies and engineered network capacity designs. These leaks often result in wide-scale outages that affect entire national-scale communication infrastructures for hours.
NIST, in collaboration with the Office of the National Cyber Director (ONCD) is working closely with the internet industry to design, standardize and foster deployment of extensions to BGP to address these security and robustness issues.
NIST staff are leading contributors to the development of Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) specifications for BGP protocol extensions to mitigate malicious attacks and route leaks. NIST developed reference implementations, test systems, measurement tools, performance analyses and deployment guidance are serving as a catalyst for the emerging global deployment of these critical technologies.
National Priorities
The scope and focus of NIST's work in Robust Inter-Domain Routing is guided by specific identified national priorities and goals, including:
The National Cybersecurity Strategy and Implementation Plan
-

National Cybersecurity Strategy Invest in a Resilient Future - Reducing systemic technical vulnerabilities in the foundation of the Internet and across the digital ecosystem while making it more resilient against transnational digital repression.
- We must take steps to mitigate the most urgent of these pervasive concerns such as Border Gateway Protocol vulnerabilities, unencrypted Domain Name System requests, and the slow adoption of IPv6.
- The Federal Government will lead by ensuring that its networks have implemented these and other security measures while partnering with stakeholders to develop and drive adoption of solutions that will improve the security of the Internet ecosystem and support research to understand and address reasons for slow adoption.
-
- The Roadmap to Enhancing Internet Routing Security priorities to:
Identify needed research and development.

ONCD Roadmap to Enhancing Internet Routing Security - Standards and Technology Development. NIST should continue to lead and coordinate USG efforts to research, standardize, and foster commercialization of BGP security and resilience mechanisms to address remaining BGP vulnerabilities, including malicious BGP path manipulations, route leak mitigation, and peering authentication. NIST should also continue to develop monitoring and measurement tools to assess the progress and correctness of the global deployment of these additional mechanisms.
- Metrics and Progress reporting ..... establish a reporting mechanism for measuring Federal agency adoption of ROA, monitoring progress, and conducting analytics, where appropriate.
- Guidance to the Federal Enterprise ... establish guidance for Federal departments and agencies to implement ROAs in a timely manner, aligned with agency risk assessments.
Major Accomplishments
See the list of Associated Products for a complete listing of our technical contributions.
-

Project staff public initial public draft of revised NIST guidance on BGP Security and Resilience updating recommendations on existing technologies such as Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI), Route Origin Authorization (ROA), and Route Origin Validation (ROV) and addressing new technologies such as Autonomous System Provider Authorization (ASPA) and new approaches to source address validation
- Project team progressed co-authored IETF specifications for BGP route-leak mitigation (BGP AS_PATH Verification Based on Autonomous System Provider Authorization (ASPA) Objects) and IP address spoofing mitigation (Source Address Validation Using BGP UPDATEs, ASPA, and ROA (BAR-SAV)).
-

- Project staff provided subject matter expertise and custom measurements/analytics to support the development of the ONCD Roadmap to Enhance Internet Routing Security and the FCC NPRM on Internet Routing Security. Both efforts highlight NIST contributions to IETF standards, test and measurement tools, and deployment guidance and their impact in advancing BGP security and resilience.
- Project team designed and submitted new IETF draft specifications to improve source address verification (anti spoofing) techniques by leveraging existing and emerging RPKI data sets.
-

Detection and Mitigation of Route Leaks in the Border Gateway Protocol - Project staff continued to advance techniques to detect and mitigate BGP routing failures caused by route leaks. New standards for local detection and mitigation procedures were published as well as software test frameworks and data sets for emerging global route leak solutions were released.
- Project team awarded Department of Commerce Gold Medal "For developing innovative technologies that resolved critical Internet vulnerabilities and dramatically improved Internet robustness."
- Project staff contributed analysis and design improvements to IETF emerging specifications for BGP route leak mitigation techniques and released reference implementations and test tools for the Autonomous System Provider Authorization (ASPA) approach.
-

- Release of a new version of the NIST RPKI Monitor developed to add more analysis features for understanding the completeness, correctness, and stability of the global RPKI-ROV infrastructure.
- Project staff published comprehensive guidance for enterprises and ISPs addressing BGP Security and DDoS Mitigation techniques (NIST SP.800-189).
- Project staff lead the design and standardization of techniques to enhance the utility of Reverse Path Filtering as a means to mitigate internet DDoS threats (RFC 8704).
- Project staff developed and employed scalable test tools to examine the scalability and robustness of emerging commercial implementations and production services for RPKI-based origin validation in support the NCCoE SIDR Project.
-

High Performance BGP Security: Algorithms and Architectures Project staff led IETF design and standardization of BGP route leak mitigation techniques and BGP-enabled DDoS mitigation techniques.
- Project staff led IETF efforts to finalize BGPsec standard specifications and update NIST reference implementations to the final version of the specification.
- Project staff and collaborators publish research on high-performance cryptography and optimization techniques to dramatically improve the performance of BGPsec implementations.
Project staff release online system to test and measure global deployment of RPKI routing security infrastructure.

NIST RPKI Measurement & Analysis System. - Project staff conducted on behalf of industry partners extensive performance / scaling analysis of emerging BGPsec prototype implementations.
- Project staff lead industry outreach workshops with the North American Network Operators Group to examine the station of products and services for BGP origin validation based upon RPKI.
- Project staff led the development of IETF specifications for Route Leak problem definition.
- Project staff led the modeling and analysis activities in support of emerging IETF protocol designs for BGP security extensions.
-

Threats & Vulnerabilities in Internet Inter-domain Routing and Significant Attacks. - Project conduct modeling and analysis of the problem space for BGP security, including modeling of large-scale attack scenarios and comparative analysis of BGP anomaly detection algorithms and other approaches that do not require changes to the existing routing system.
Current Project Plans
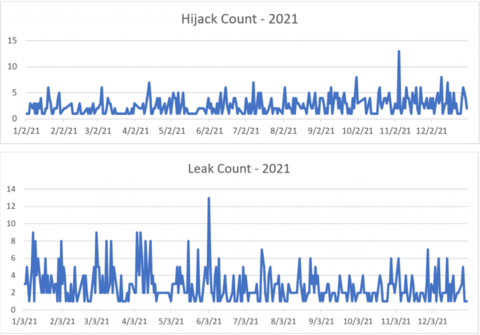
Recent growth in the number [2] and sophistication [3] [4] of attacks on the Internet’s Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) infrastructure has resulted in the National Cybersecurity Strategy [7] identifying the goal of improving the security and resilience of the Internet’s global routing infrastructure as a top priority and assigning NIST the task of accelerating the development, standardization and commercialization of technologies and guidance necessary to achieve that goal [5].
There has been much recent progress in the design, standardization, and commercialization of new BGP security mechanisms. IETF specifications for BGP Route Origin Validation (ROV) have been largely completed, a global Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) service has been deployed by the 5 Regional Internet Registries and today approximately 53% of the over 1 million routes announced in BGP are protected by cryptographically verifiable Route Origin Authorizations (ROAs) [6].
BGP ROV and the RPKI allow one to detect and filter simple route hijacks and accidental misconfigurations that also result in unauthorized BGP originations. ROV was the first new BGP security technology developed by the IETF, but it’s simple mechanisms (specifically designed to limit the processing burden on routers) are not robust enough to stop sophisticated attackers who seek to forge other aspects of BGP announcements for the purpose of hijacking or re-routing traffic.
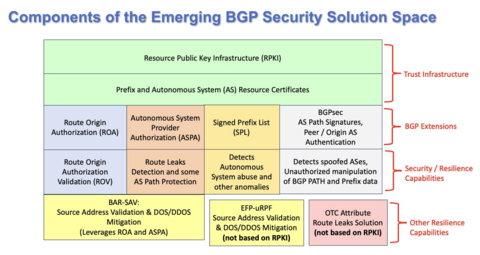
Internet routing security is a complex problem requiring multiple complementary solutions (e.g., ROA, ROV, ASPA, BGPsec, BAR-SAV, etc.). These solutions leverage a common infrastructure called the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) for registration of cryptographically signed attestation objects. NIST has made significant contributions (as technology inventors and lead authors of IETF RFCs and drafts) to these solutions.
NIST’s current research and standardization efforts focus on other serious threats to the security and resilience of the internet’s routing infrastructure: large scale failures caused by route-leaks and distributed denial of services attacks. In FY 2025, NIST plans to work in collaboration with industry partners to advance IETF specifications for new components of the emerging suite of BGP security technologies. These techniques (ASPA, SPL and ASRA) are described below.
Signed Prefix List (SPL) and SPL Route Origin Validation
The NIST BGP security team members have recently begun collaborating with Fastly on the Signed Prefix List (SPL) based Route Origin Validation (SPL-ROV) [7]. SPL is an extension to RPKI that enables an AS to publish a digitally signed list of the all the prefixes it originates or may originate. This is like a ROA, only it is signed by the AS holder, rather than the prefix holder. SPL extends ROV with a second data source that mitigates AS forgery and reduces the attack surface for forged-origin hijacking attacks (Figure 1). Thus SPL-based ROV (SPL-ROV) will complement ROA-based ROV (ROA-ROV) and further extend BGP security.
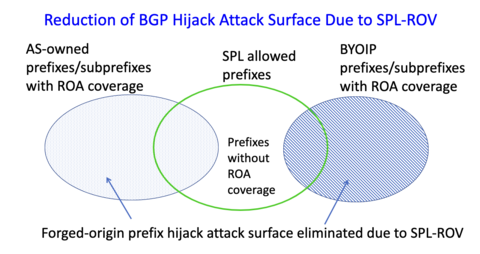
Figure 1: Reduction of forged-origin hijacking attack surface due to SPL-ROV.
Deliverables from this task will include:
- NIST will update recently submitted Internet Draft based on IETF working group (WG) feedback and advance it to the IETF SIDROPS WG last call by 3Q25.
Projected Impact:
- Signed prefix lists will enhance the ability of ISPs to provide another, complementary form of route origin authentication information. Once implemented, SPL capabilities will increase coverage of ROA data on the Internet.
Autonomous System Relationship Authorization (ASRA)
NIST BGP security team members are in discussions in the IETF with industry partners (Juniper Networks, Akamai, Huawei, University of Connecticut) to propose a new RPKI-based attestation object called Autonomous System Relationship Authorization (ASRA) which will complement ASPA [8] by expanding its AS path manipulation detection capability. Currently, there is a significant gap in the ASPA design in that it fails to detect AS path manipulation using a faked-link (i.e., a faked BGP connection) and advertising BGP updates with forged-origin or forged-path-segment to customer autonomous systems (ASes) (see Figure 2). ASRA seeks to accomplish this by allowing ASes to register their list of customers and lateral peers. The details of the algorithm that combines ASPA and ASRA are being worked out with NIST leading the effort. This methodology will be proposed to the IETF in form of a new Internet Draft and the work will be pursued through FY 2025.
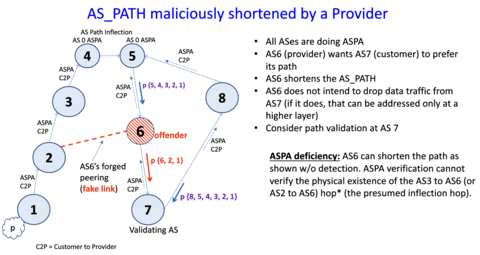
Figure 2: An ASPA vulnerability of allowing a forged peering (false link) to go undetected is mitigated by ASRA.
Deliverables from this task will include:
- Submission of a new Internet Draft describing the ASRA object and the associated path verification algorithm and advance it to the IETF SIDROPS WG last call stage by 4Q25.
Projected Impact:
- Progression of ASRA specifications will close an existing security gap in the feasible path validation algorithms of ASPA.
- NIST will continue to further strengthen its position as one of the most active contributors and leaders in the IETF to advance Internet routing security technology and standards.
Completing Route Leak and DDoS Mitigation Standards
While technologies to address forged routing announcements have been standardized and are at varying stages of commercialization and deployment, there are other systemic vulnerabilities in the global BGP routing system that often trigger cascading failures of significant scale [9] [10]. NIST led the effort in the IETF to define the problem posed by “route leaks” [11] and to focus the community on developing standardized solutions. We are currently pursuing two distinct solutions for detecting and mitigating route leaks. The first solution involves a simple signaling mechanism within a single network to detect a subset of potential route-leak scenarios [12]. A second more complete solution proposes to extend the RPKI to include digitally signed autonomous system provider authorization (ASPA) objects [13] that document the peering relationship between inter-connected networks and provides a validation algorithm [14] to allow any network to attempt to verify that a BGP announcement it receives does not violate the common peering arrangements between networks and their neighboring ISPs (Figure 3).
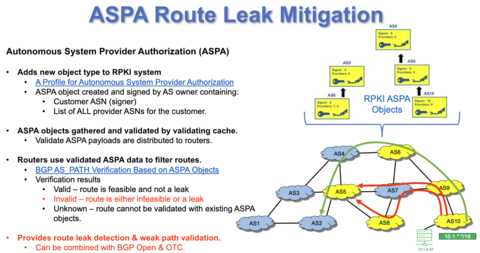
Figure 3 ASPA-based Route Leak Mitigation
Another systemic vulnerability of the Internet routing infrastructure is the lack of viable mechanisms to enable routers to detect packets in the data plane with “spoofed” source addresses. Address spoofing is a common technique for malicious actors to try to circumvent some security mechanisms or to bounce traffic off high performance Internet servers toward a target victim at such a rate that the target system collapses under the load [15]. These attacks are known as “reflection attacks,” and while there has been guidance [16] to filter packets with spoofed source addresses for over 20 years, we have lacked robust algorithms to compute the sets of filters necessary given the complexity of modern Internet routing topologies.
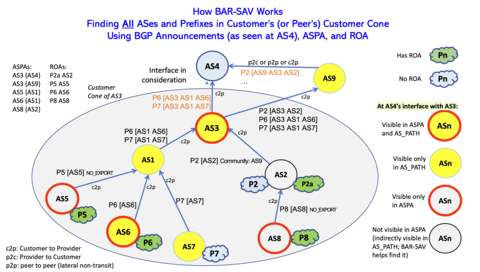
Figure 4: BAR-SAV - New Approach to DDoS Mitigation
To address this issue NIST led the design and standardized a viable algorithm to compute such filters [17]. With the emergence of the proposed RPKI extensions to address the route leak problem, NIST developed a new source address validation algorithm (BAR-SAV) that is more robust than our first scheme over a wider variety of network deployment scenarios [18].
Deliverables from this task will include:
The IETF specifications related to the BAR-SAV and ASPA topics are multi-year NIST lead efforts in the IETF. Both specifications are reasonably mature and near ready to progress towards final RFC status. Remaining NIST efforts for FY25 include:
- Process comments received in working group last call (WGLC) of the ASPA verification specification and submit for publication.
- When ASPA standards are finalized, NIST will update our open-source reference implementations [19] of the ASPA specifications and extend our test tools and synthetic data sets to address the latest changes in the standards.
- The BAR-SAV specification is mature and could be sent to WGLC as soon as the ASPA specification upon which it depends is submitted for publication. When this is possible NIST will handle progression and comment resolution associated with WGLC.
Projected Impact:
- ASPA and BAR-SAV standards once commercialized in BGP routers and supporting routing infrastructure software will provide focused solutions to route-leak and DDoS vulnerabilities that threaten the Internet today.
Revising NIST Security Guidance on Inter-Domain Routing
In 2019 NIST published its first comprehensive security guidance on Internet routing. NIST SP-800-189 Resilient Interdomain Traffic Exchange: BGP Security and DDoS Mitigation. The National Cybersecurity Strategy Implementation plan and an emerging executive order on cyber security task NIST to update this guidance to address current commercially viable BGP security solutions and to address emerging standards to include ASPA and BAR-SAV. Updating of the NIST special publication 800-189 is ongoing work.
Deliverables from this task will include:
- An initial draft of a revised SP-800-189 will be published for public comment in Q2FY25.
Projected impact:
- Revised NIST guidance on Inter-Domain routing will serve as a technical basis to support emerging USG RPKI deployment plans.
Accelerating US Adoption of BGP Security Mechanisms
There are significant efforts underway in the FCC [20], CISA [21], and the ONCD [22] to develop plans to drive adoption of emerging BGP security technologies in the US, and in particular, in USG networks where adoption to date is seriously lagging. NIST is recognized as the USG’s technical expert in these issues and is collaborating with these organizations, and GSA, OMB, and ARIN to provide data and analysis to guide USG adoption plans and to provide technical guidance to support their implementation.
In FY24 tasks in this area included providing measurement data, analyses, and subject matter expertise to FCC and OMB teams and software updates to the NIST Internet Routing Data Analysis Framework (see below) to provide specific data and analyses requested by these other USG agencies. These partner agencies have requested continued SME support in FY25 as their plans transition to implementation. The FCC, ONCD and have requested NIST to add new features and forms of analysis to the NIST RPKI Monitor to support their current implementation plans.
Deliverables from this task will include:
- Continued SME support of FCC and ONCD efforts and implementation plans.
- Software enhancements to the NIST RPKI Monitor (see below).
Projected impact:
- Contributing to technically sound implementation plans and deployment procedures will expedite adoption of routing security technologies in the US.
Internet Routing Data Analysis Framework
The NIST RPKI Monitor [23] and its underlying Internet Routing Data Analysis Framework, provides a test and measurement infrastructure designed to monitor the dynamics of the global RPKI and the impact of RPKI-based BGP security mechanisms on Internet routing. Its purpose is to provide measurement data and analyses to the research, standardization, and operations communities necessary to improve the trust and confidence in the underlying technologies. Our NIST RPKI Monitor is widely used and cited in the industry as an authoritative source for data and analysis of the completeness and correctness of global RPKI data and its potential impact on global routing.
In FY24, in response to FCC and ONCD requests, NIST enhanced the NIST RPKI Monitor to provide custom views of subsets of global and regional metrics. Specific new analyses were developed to examine specific perceived barriers to adoption by large ISPs.
In FY25 NIST will enhance the RPKI monitor to include analyses of ASPA RPKI objects and ASPA path validation. In addition, project staff will implement the generalized ability for users the ability to define subset “views” of the global data based upon user defined sets of addresses or origin networks and allow users to subscribe to event notifications for changes in the resources in their defined view.
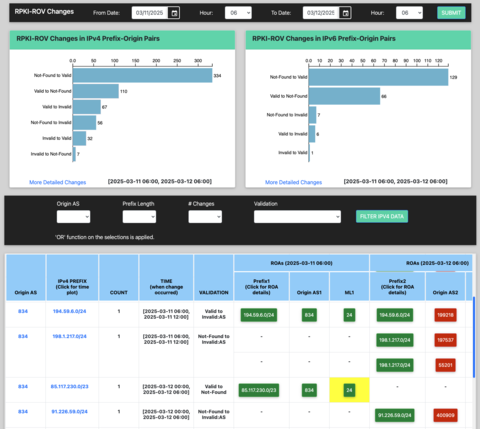
Figure 5: NIST RPKI Monitor
Deliverables from this task will include:
- Continued new feature enhancements to the RPKI Monitor as requested by USG and industry partners.
Projected impact:
- The NIST RPKI Monitor is widely relied on by USG and the Internet industry to provide accurate characterizations of the state of global deployment of emerging BGP security technologies. Trusted measurements from NIST tool provide the technical basis for informed plans and implementation procedures.
References
[1] S. L. Murphy, “BGP Security Vulnerabilities Analysis,” Internet Engineering Task Force, Request for Comments RFC 4272, Jan. 2006. doi: 10.17487/RFC4272. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc4272. [Accessed: May 10, 2024]
[2] “BGP Security in 2021,” MANRS, Feb. 21, 2022. Available: https://www.manrs.org/2022/02/bgp-security-in-2021/. [Accessed: Jul. 08, 2022]
[3] H. Birge-Lee, Y. Sun, A. Edmundson, J. Rexford, and P. Mittal, “Bamboozling Certificate Authorities with {BGP},” presented at the 27th {USENIX} Security Symposium ({USENIX} Security 18), 2018, pp. 833–849. Available: https://www.usenix.org/conference/usenixsecurity18/presentation/birge-l…. [Accessed: Feb. 21, 2019]
[4] “KlaySwap - Another BGP Hijack Targeting Crypto Wallets,” MANRS, Feb. 17, 2022. Available: https://www.manrs.org/2022/02/klayswap-another-bgp-hijack-targeting-cry…. [Accessed: Jul. 08, 2022]
[5] “National Cybersecurity Strategy Implementation Plan,” Executive Office of the President, Jul. 2023. Available: https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/National-Cybersec…. [Accessed: Sep. 11, 2023]
[6] “NIST RPKI Monitor.” Available: https://rpki-monitor.antd.nist.gov/. [Accessed: Jul. 08, 2022]
[7] K. Sriram, J. Snijders, and D. Montgomery, “Signed Prefix List (SPL) Based Route Origin Verification and Operational Considerations,” Internet Engineering Task Force, Internet Draft draft-ietf-sidrops-spl-verification-00, Jun. 2024. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-sidrops-spl-verification. [Accessed: Sep. 23, 2024]
[8] A. Azimov, E. Bogomazov, R. Bush, K. Patel, J. Snijders, and K. Sriram, “BGP AS_PATH Verification Based on Autonomous System Provider Authorization (ASPA) Objects,” Internet Engineering Task Force, Internet Draft draft-ietf-sidrops-aspa-verification-18, Jul. 2024. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-sidrops-aspa-verification. [Accessed: Sep. 23, 2024]
[9] D. Goodin, “Google goes down after major BGP mishap routes traffic through China,” Ars Technica, Nov. 13, 2018. Available: https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2018/11/major-bgp-mishap…. [Accessed: Apr. 25, 2022]
[10] Y. Huang, “Internet Outrage Caused by Verizon Shows How Fragile the Internet Routing Is,” Medium, Jul. 02, 2019. Available: https://medium.com/hackernoon/internet-outrage-caused-by-verizon-shows-…. [Accessed: Jan. 07, 2021]
[11] K. Sriram, D. Montgomery, D. McPherson, E. Osterweil, and B. Dickson, “Problem Definition and Classification of BGP Route Leaks,” RFC Editor, RFC7908, Jun. 2016. doi: 10.17487/RFC7908. Available: https://www.rfc-editor.org/info/rfc7908. [Accessed: Jan. 16, 2018]
[12] A. Azimov, E. Bogomazov, R. Bush, K. Patel, and K. Sriram, “Route Leak Prevention and Detection Using Roles in UPDATE and OPEN Messages,” Internet Engineering Task Force, Request for Comments RFC 9234, May 2022. doi: 10.17487/RFC9234. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc9234. [Accessed: May 09, 2022]
[13] A. Azimov, E. Bogomazov, R. Bush, K. Patel, J. Snijders, and K. Sriram, “BGP AS_PATH Verification Based on Autonomous System Provider Authorization (ASPA) Objects,” Internet Engineering Task Force, Internet Draft draft-ietf-sidrops-aspa-verification-16, Aug. 2023. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-sidrops-aspa-verification. [Accessed: Sep. 11, 2023]
[14] A. Azimov, E. Bogomazov, R. Bush, K. Patel, and J. Snijders, “Verification of AS_PATH Using the Resource Certificate Public Key Infrastructure and Autonomous System Provider Authorization,” Internet Engineering Task Force, Internet Draft draft-azimov-sidrops-aspa-verification-01, Oct. 2018. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-azimov-sidrops-aspa-verification. [Accessed: Jul. 08, 2022]
[15] C. Cimpanu, “Google says it mitigated a 2.54 Tbps DDoS attack in 2017, largest known to date,” ZDNet. Available: https://www.zdnet.com/article/google-says-it-mitigated-a-2-54-tbps-ddos…. [Accessed: Oct. 19, 2020]
[16] D. Senie and P. Ferguson, “Network Ingress Filtering: Defeating Denial of Service Attacks which employ IP Source Address Spoofing,” Internet Engineering Task Force, Request for Comments RFC 2827, May 2000. doi: 10.17487/RFC2827. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc2827. [Accessed: Jul. 08, 2022]
[17] K. Sriram, D. Montgomery, and J. Haas, “Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding,” Internet Engineering Task Force, Request for Comments RFC 8704, Feb. 2020. doi: 10.17487/RFC8704. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc8704. [Accessed: Nov. 09, 2021]
[18] K. Sriram, I. Lubashev, and D. Montgomery, “Source Address Validation Using BGP UPDATEs, ASPA, and ROA (BAR-SAV),” Internet Engineering Task Force, Internet Draft draft-ietf-sidrops-bar-sav-00, Feb. 2023. Available: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-sidrops-bar-sav. [Accessed: Mar. 07, 2023]
[19] “BGP Secure Routing Extension (BGP‑SRx) Software Suite,” NIST, Aug. 2016, Available: https://www.nist.gov/services-resources/software/bgp-secure-routing-ext…. [Accessed: Jul. 08, 2022]
[20] “FCC Launches Inquiry into Internet Routing Vulnerabilities,” Federal Communications Commission, Feb. 28, 2022. Available: https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-launches-inquiry-internet-routing-vuln…. [Accessed: Mar. 07, 2022]
[21] “CISA’s Jen Easterly, FCC’s Jessica Rosenworcel on Need to Advance Border Gateway Protocol Security,” Aug. 03, 2023. Available: https://executivegov.com/2023/08/cisas-jen-easterly-fccs-jessica-rosenw…. [Accessed: Aug. 04, 2023]
[22] “Roadmap to Enhancing Internet Routing Security,” Office of the National Cyber Director, Sep. 2024. Available: https://bidenwhitehouse.archives.gov/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Roadmap…. [Accessed: Sep. 16, 2024]
[23] “NIST RPKI Deployment Monitor.” Aug. 15, 2016. Available: https://www.nist.gov/services-resources/software/nist-rpki-deployment-m…. [Accessed: Sep. 13, 2023]
Robust Inter Domain Routing
| Product | Reference |
|---|---|
| Standards Specification | Azimov A., Bogomazov E., Bush R., Patel K., Snijders J., Sriram K., BGP AS_PATH Verification Based on Autonomous System Provider Authorization (ASPA) Objects, IETF Internet Draft, September 2025.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Borchert O., Matejka M., ASPA-based AS path verification examples, IETF SIDROPS WG supporting document (online), August 2025. |
| Standards Contribution, Presentation | Sriram K., Lubashev I., Montgomery D., Update on the BAR-SAV Draft, SAVNET WG Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 123, July 2025.
|
| Standards Contribution, Presentation | Sriram K., Matejka M., Zhang J., Draft Update: ASPA-based AS Path Verification, SIDROPS WG Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 123, July 2025.
|
| Software | Borchert O., Lee K., Sriram K., Hannachi L., Montgomery D., BGP-RPKI Input-Output (BRIO), Test Tool and Data Sets for ASPA, RPKI ROV, and BGPsec Interoperability Testing, July 2025. |
| Standards Specification | Geng N., Qin L., Sriram K., Li D., Source Prefix Advertisement for Inter-domain SAVNET, IETF Internet Draft, SIDROPS WG, July 2025.
|
| Standards Specification | Wu J., Li D., Liu L., Huang M., Sriram K., Source Address Validation in Inter-domain Networks Gap Analysis, Problem Statement, and Requirements, IETF Internet Draft, July 2025.
|
| Conference Publication | Hannachi L., Sriram K., Montgomery D., Analysis of Propagation of Regular, Extended, and Large BGP Communities, 12th IFIP International Conference on New Technologies, Mobility and Security (NTMS 2025), June 2025.
|
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Snijders J., Montgomery D., Signed Prefix List (SPL) Based Route Origin Verification and Operational Considerations, Internet Draft, Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), June 2025.
|
| Standards Specification | Kumari W., Sriram K., Hannachi L., Haas J., Deprecation of AS_SET and AS_CONFED_SET in BGP, IETF RFC 9774, May 2025.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Geng N., Herzberg A., Autonomous System Relationship Authorization (ASRA) as an Extension to ASPA for Enhanced AS Path Verification, IETF Internet Draft, SIDROPS WG, April 2025.
|
| Standards Contribution | Geng N., Sriram K., Huang M., A Profile for Autonomous System Relationship Authorization (ASRA), IETF Internet Draft, SIDROPS WG, April 2025.
|
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Lubashev I., Montgomery D., Source Address Validation Using BGP UPDATEs, ASPA, and ROA (BAR-SAV), IETF Internet Draft (Standards Track, SIDROPS Working Group), March 2025.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Borchert O., Matejka M., ASPA-based AS path verification examples and unit tests, IETF SIDROPS Meeting, IETF 122, March 2025, March 2025.
|
| Standards Contribution | Li D., Wu J., Liu L., Huang M., Sriram K., Source Address Validation in Inter-domain Networks: Gap Analysis, Problem Statement, and Requirements, IETF SAVNET WG Meeting, IETF 122, March 2025, March 2025. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Lubashev I., Montgomery D., An update on the SAV using BGP UPDATE messages, ASPA, and ROA (BAR-SAV), IETF SAVNET WG Meeting, IETF 122, March 2025, March 2025.
|
| Standards Specification | Li D., Wu J., Liu L., Huang M., Sriram K., Source Address Validation in Inter-domain Networks Gap Analysis, Problem Statement, and Requirements, IETF Internet Draft - Informational - SAVnet Working Group, March 2025.
|
| Standards Specification | Bruijnzeels T., de Kock T., Borchert O., Ma D., Human Readable Validate ROA Payload Notation, IETF SIDROPS Working Group, March 2025.
|
| Standards Specification | Borchert O., T.Bruijnzeels, D.Ma, de Kock T., Human Readable ASPA Notation, IETF SIDROPS Working Group, March 2025.
|
| Presentation | Montgomery D., Sriram K., BGP Security Level Set: Problem Space and Emerging Solutions, Presentation to DHS Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (DHS-CISA), February 2025. |
| NIST Publication | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Border Gateway Protocol Security and Resilience, NIST SP 800-189 Rev. 1 (Initial Public Draft), January 2025.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Geng N., Herzberg A., Autonomous System Relationship Authorization (ASRA) as an Extension to ASPA for Enhanced AS Path Verification, SIDROPS WG Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 121, Dublin, Ireland, November 2024. |
| Workshop | Montgomery D., NSF Workshop: Policy-Relevant Internet Measurement, Invited participant., May 2024.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Draft Update: ASPA-Based AS_PATH Verification, IETF SIDROPS Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 119, March 2024.
|
| Panel Session | Montgomery D., NCTA-CableLabs Forum: Internet Routing Security, Industry Webinar, January 2024.
|
| Presentation | Montgomery D., The Role of Standardization, NSF Workshop: Towards Re-architecting Todays Internet for Survivability, Northwestern University, November 2023.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Snijders J., Montgomery D., Design Analysis of RPKI PrefixList and Operational Considerations, IETF SIDROPS Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 118, November 2023.
|
| Conference Publication, Presentation, Poster | Hoeger N., Rodday N., Borchert O., Dreo Rodosek G., Path Plausibility Algorithms in GoBGP, 19th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM), Niagra Falls, Canada, November 2023.
|
| Presentation | Sriram K., ASPA-based BGP AS_PATH Verification and Route Leaks Solution, NANOG 89, San Diego, CA, October 2023.
|
| Presentation | Sriram K., ASPA-based BGP AS_PATH Verification and BAR-SAV for Mitigation of IP Address Spoofing, Internet2 Webinar, August 2023.
|
| Presentation | Montgomery D., NIST Efforts to Accelerate Standardization and Support Adoption of BGP Security Technologies, Federal Communications Commission Border Gateway Protocol Security Workshop, July 2023.
|
| Presentation | Montgomery D., BGP Security Level Set Problem Space and Emerging Solutions, Invited presentation to Federal Communications Commission Border Gateway Protocol Security Workshop, July 2023.
|
| Presentation | Bruijnzeels T., Borchert O., Ma D., de Kock T., Human Readable ASPA Notation, IETF 117 Conference, SIDROPS Working Group, San Francisco, July 2023.
|
| Presentation | Bruijnzeels T., Borchert O., Ma D., de Kock T., Human Readable Validate ROA Payload Notation, IETF 117 - SIDROPS Working Group, San Francisco, July 2023.
|
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Montgomery D., AS Hijack Detection and Mitigation, IETF Internet Draft (Standards Track, SIDROPS Working Group), July 2023. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Azimov A., Bogomazov E., Bush R., Patel K., Snijders J., Update on BGP AS_PATH Verification Based on ASPA Objects, SIDROPS WG Meeting, IETF 117, San Francisco, CA, July 2023.
|
| Panel Session | Montgomery D., et. al., Working with Governments to Progress Routing Security, Internet Society Routing Security Summit 2023, July 2023.
|
| Presentation | Sriram K., An Overview of ASPA-based BGP AS_PATH Verification, Routing Security Workshop hosted by Amazon, Seattle, WA, June 2023. |
| Workshop | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Amazon Internet Routing Security Roundtable, Invitation only workshop before NANOG 88., June 2023. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Azimov A., Bogomazov E., Bush R., Patel K., Snijders J., ASPA-based AS Path Verification Draft Update, SIDROPS WG Meeting, IETF 116, Yokohama, Japan, March 2023.
|
| Presentation | Montgomery D., Cannon R., Practical BGP Security with RPKI - Problem Space, Emerging Solutions, USG Call to Action, Invited presentation to Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) Team Telecom work group, March 2023.
|
| Presentation | Sriram K., ASPA, BAR-SAV, and IETF Standards, Invited seminar/guest lecture to a graduate student class, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, February 2023.
|
| Workshop | Montgomery D., Workshop: Securing the Public Key Infrastructure, Princeton Center for Information Technology Policy, December 2022. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Lubashev I., Montgomery D., Lowering Improper Block and Improper Admit for SAV The BAR-SAV Approach, SAVNET WG, Proceedings of the IETF 115, London, UK, November 2022., November 2022.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Lubashev I., Montgomery D., An Update on Source Address Validation Using BGP Updates, ASPA, and ROA (BAR-SAV), SIDROPS WG, Proceedings of the IETF 115, London, UK, November 2022., November 2022.
|
| Standards Contribution | Kumari W., Sriram K., Hannachi L., Haas J., Deprecation of AS_SET in BGP, IDR WG, Proceedings of the IETF 115, London, UK, November 2022., November 2022.
|
| Report | Montgomery D., et. al. members of BITAG Technical Working Group on Routing Security, The Security of the Internets Routing Infrastructure: A Broadband Internet Technical Advisory Group Technical Working Group Report, Security of the InteBroadband Internet Technical Advisory Group Technical Working Group Report., November 2022.
|
| Standards Specification | Gilad Y., Goldberg S., Sriram K., Snijders J., Maddison B., The Use of Maxlength in the RPKI, IETF Request for Comments, RFC-9319 / BCP 185, October 2022.
|
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Design Discussion of Route Leaks Solution Methods, IETF Internet Draft (Informational), September 2022. |
| Standards Specification | Heitz J., Sriram K., Dickson B., Heasley J., BGP Well Known Large Community, IETF Internet Draft, September 2022.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Lubashev I., Montgomery D., Source Address Validation Using BGP UPDATEs, ASPA, and ROA (BAR-SAV), IETF SIDROPS WG Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 114, July 2022.
|
| Standards Specification | Azimov A., Bogomazov E., Bush R., Patel K., Sriram K., Route Leak Prevention and Detection using Roles in UPDATE and OPEN Messages, IETF Request for Comments (RFC-9234), May 2022.
|
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Azimov A., Methods for Detection and Mitigation of BGP Route Leaks, IETF Internet-Draft (Standards Track, IDR Working Group), April 2022.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., ASPA Verification Procedures: Enhancements and RS Considerations, IETF 113 SIDROPS WG Meeting, March 2022.
|
| Software | Borchert O., Hannachi L., Lee K., Sriram K., Montgomery D., BGP Secure Routing Extension (BGP-SRx) Suite 6.2 - BGP-SRx - Test Framework Generator for ASPA, NIST Open Source Reference Implementation, March 2022. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., BGP Route Leak Prevention and Mitigation: An Overview of Standards Efforts in the IETF, Milan IX (MIX) Salotto 2021, Milan, Italy, November 2021. |
| Standards Contribution | Borchert O., Hannachi L., Lee K., Montgomery D., Sriram K., BGP-ASPA Hackathon Report, IETF 112 - SIDROPS Working Group, November 2021. |
| Standards Contribution | Borchert O., Hannachi L., Lee K., Sriram K., Montgomery D., IETF Hackathon BGP-ASPA Interop Testing, Hackathon 112 Project, November 2021. |
| NIST Publication | Borchert O., Lee K., Sriram K., Montgomery D., Gleichmann P., Adalier M., BGP Secure Routing Extension (BGP-SRx): Reference Implementation and Test Tools for Emerging BGP Security Standards, NIST Technical Note 2060, September 2021.
|
| Software | Borchert O., Lee K., BGP Secure Routing EXtensions (BGP-SRx) Reference Implementations and Test Tools versions 6.1.4 and 5.1.13, NIST Open Source Reference Implementation, September 2021. |
| Standards Contribution | Hannachi L., Sriram K., Analysis of Propagation of Regular, Extended, and Large BGP Communities, Presentation at the IETF GROW WG Meeting, IETF 111 Proceedings, July 2021, July 2021. |
| Blog | Montgomery D., NIST RPKI Deployment Monitor update, Asia Pacific Network Information Center (APNIC) Blog, May 2021.
|
| Software | Hannachi L., Sriram K., Borchert O., Montgomery D., NIST RPKI Monitor, NIST Software Release, April 2021. |
| Software | Borchert O., Lee K., BGP-SRx Software Suite 5.1.4, NIST Reference Implementation, March 2021. |
| Standards Contribution | Gilad Y., Goldberg S., Sriram K., Snijders J., Maddison B., RPKI Maxlength Update, IETF SIDROPS Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 110, March 2021., March 2021.
|
| Presentation | Sriram K., Heitz J., On the Accuracy of Algorithms for ASPA Based Route Leak Detection, IETF SIDROPS Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 110, March 2021.
|
| Software | Borchert O., Lee K., NIST BGP-SRx Software Suite Version 5.1.1, NIST Reference Implementation, August 2020. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Montgomery D., AS Hijack Detection and Mitigation, Presentation to the IETF SIDROPS Working Group Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 108, July 2020. |
| Standards Contribution | Borchert O., Montgomery D., Kopp D., Signaling BGPsec Validation State, Presentation to the IETF SIDROPS Working Group Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 108, July 2020, July 2020.
|
| Presentation | Sriram K., Practical Solutions for Internet Routing Security and DDoS Mitigation, Cyber Security Webinar, Organized by the Internet Society, May 2020.
|
| Software | Lee K., ExaBGP-SRx, NIST Reference Implementation, May 2020. |
| Software | Lee K., GoBGP-SRx, NIST Reference Implementation, May 2020. |
| Standards Contribution | Heitz J., Sriram K., Dickson B., Heasley J., BGP Well Known Large Community, IETF IDR Interim Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF, April 2020.
|
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Haas J., Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering, IETF RFC 8704, February 2020.
|
| NIST Publication | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Resilient Interdomain Traffic Exchange: BGP Security and DDoS Mitigation, NIST SP 800-189, December 2019. |
| Presentation | Montgomery D., Towards Viable Information Infrastructures for Trustworthy Networking, Workshop on Internet Economics: Knowledge of Internet Structure: Measurement, Epistemology, and Technology (WIE-KISMET), University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA., December 2019. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Kumari W., Hannachi L., Haas J., Deprecation of AS_SET and AS_CONFED_SET, IETF IDR Working Group Meeting, Proceedings of IETF 106, Singapore, November 2019.
|
| Standards Contribution | Borchert O., Montgomery D., Kopp D., Signaling route origin and path validation state, Presentation to the IETF SIDROPS Working Group Meeting, Proceedings of the IETF 106, Singapore, Nov 2019, November 2019.
|
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Design Discussion and Comparison of Protection Mechanisms for Replay Attack and Withdrawal Suppression in BGPsec, IETF Internet Draft, October 2019. |
| Standards Specification | Borchert O., Montgomery D., Kopp D., BGPsec Validation State Signaling, IETF SIDROPS Working Group, October 2019.
|
| Standards Contribution | Azimov A., Sriram K., Bogomazov E., Bush R., Patel K., BGP Roles and More, IETF IDR Working Group Meeting, Proceedings of IETF 105, Montreal, Canada, July 2019.
|
| Standards Contribution | Azimov A., Sriram K., Montgomery D., Dickson B., Patel K., Robachevsky A., Bogomazov E., Bush R., Route Leak Detection with Community, GROW Working Group Meeting, Proceedings of IETF 105, Montreal, Canada, July 2019.
|
| Standards Specification | Turner S., Borchert O., BGPsec Algorithms, Key Formats, and Signature Formats, RFC 8608, June 2019.
|
| Standards Contribution | Hannachi L., Sriram K., Borchert O., Montgomery D., RPKI/ROV data analysis with detailed characterization of Invalid routes, IETF SIDROPS WG Meeting, Proceedings of IETF 104, Prague, March 2019. |
| Standards Contribution | Borchert O., Montgomery D., BGPsec Validation State Signaling, Presentation at the IETF-104, SIDROPS Working Group Meeting, Prague, March 2019. |
| Audio | Montgomery D., Temin T., NIST has new guidance for protecting interdomain traffic, Federal Drive - Federal News Network Podcast, February 2019.
|
| Workshop | Montgomery D., Levy M., Snijders J., RPKI Operational Round Table, Industry workshop at NANOG 75, San Francisco CA, February 2019. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Internet Routing Security: Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Techniques, Invited lecture organized by ISOC (India Chapter) at IIIT, Hyderabad, India, November 2018. |
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Borchert O., Montgomery D., Origin Validation Policy Considerations for Dropping Invalid Routes, IETF Internet Draft (Standards Track, SIDROPS Working Group), November 2018. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Borchert O., Montgomery D., Snijders J., Origin Validation Policy Considerations for Dropping Invalid Routes, IETF SIDROPS WG Meeting, IETF 103, Bangkok, November 2018. |
| Standards Contribution | Borchert O., Montgomery D., Proposing validation state Unverified, Presentation at the IETF-103, SIDROPS Working Group Meeting, Bangkok, November 2018. |
| Standards Contribution | Borchert O., Lee K., Montgomery D., Sriram K., Observations during Testing of Route Origin Validation, Presentation at the IETF-103, SIDROPS Working Group Meeting, Bangkok, November 2018. |
| Presentation | Hannachi L., Borchert O., Sriram K., Kim O., Montgomery D., Big Data Analytics of Dynamics in the RPKI System and Their Impacts on Global Internet Routing, NIST ITL Science Day, November 2018. |
| Presentation | Montgomery D., Practical BGP Security with RPKI: If there is a will to mitigate hijacks, there is a way., Internet2 2018 Technology Exchange, Orlando FL., October 2018. |
| Presentation | Montgomery D., Robust Inter-Domain Routing: Addressing Systemic Vulnerabilities in BGP, North American Network Operators (NANOG) On the Road, Crystal City, VA, September 2018. |
| Presentation | Montgomery D., Towards Trustworthy Networks: NIST/USG Efforts and Opportunities for Collaboration, North American Network Operators (NANOG) On the Road, Crystal City, VA, September 2018. |
| NIST Publication | Haag W., Montgomery D., Barker William_C., Tan A., Protecting the Integrity of Internet Routing: Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Origin Validation, NIST Special Publication, NIST-SP-1800-14, July 2018. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Azimov A., Montgomery D., Dickson B., Patel K., Robachevsky A., Bogomazov E., Bush R., Route Leaks Solution: Merger of RLP and eOTC Drafts, Presentation at the IETF-102, IDR WG Meeting, Montreal, July 2018. |
| Standards Contribution | Gilad Y., Goldberg S., Sriram K., Snijders J., Maddison B., Use of MaxLength in the RPKI, Presentation at IETF-102, SIDROPS WG Meeting, Montreal, July 2018.
|
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., BGPsec Design Choices and Summary of Supporting Discussions, IETF RFC 8374, April 2018.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Borchert O., Montgomery D., Snijders J., Origin Validation Policy Considerations for Dropping Invalid Routes, Presentation at the IETF-101, SIDROPS Working Group Meeting, London, March 2018. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Dickson B., Patel K., Robachevsky A., Detection and Mitigation of BGP Route Leaks, Presentation at the IETF-101, IDR Working Group Meeting, London, March 2018. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Haas J., Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering, Presentation at the IETF-101, OPSEC Working Group Meeting, London, March 2018. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Internet Security: Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Techniques, Invited talk at the Indian Banking Association (IBA), Mumbai, India (attended by CIOs, CTOs, and IT security staff from many financial institutions)., November 2017. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Haas J., Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering, Presentation at the IETF-100, OPSEC Working Group Meeting, Singapore, November 2017. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Haas J., Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering, Internet Engineering Planning Group (IEPG) Meeting at IETF 100, Singapore, November 2017. |
| Software | Borchert O., Lee K., NIST BGP-SRx Software Suite Version 5, NIST Reference Implementation, October 2017. |
| Standards Specification | Lepinski M., Sriram K., BGPsec Protocol Specification, Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), RFC8205, September 2017.
|
| Standards Specification | Turner S., Borchert O., BGPsec Algorithms, Key Formats, and Signature Formats, RFC 8208, September 2017. |
| Standards Contribution | Turner S., Borchert O., BGPsec Algorithms, Key Formats, and Signature Formats, Note - Obsoleted by RFC 8208, September 2017.
|
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering, IETF-99 OPSEC Working Group Meeting, Prague, CZ, July 2017. |
| Presentation | Borchert O., Update on BGPsec Reference Implementation BGP-SRx and BGPSEC-IO - More than just a BGPsec Traffic Generator, IETF99 Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, July 2017. |
| Journal Publication | Sriram V., Montgomery D., Design and analysis of optimization algorithms to minimize cryptographic processing in BGP security protocols, Computer Communications, volume 106, pages 75-85, July 2017. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Internet Routing Vulnerabilities and Security Extensions to the Border Gateway Protocol (BGPsec), Presentation given to Indian Institute of Science (Bangalore, India) Visitors, June 2017. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Dickson B., Patel K., Robachevsky A., Methods for Prevention, Detection and Mitigation of BGP Route Leaks, IETF-98 IDR Working Group Meeting, Chicago, USA, March 2017. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Decoupling BGPsec Documents and Extended Messages draft, IETF-98 SIDROPS Working Group Meeting, Chicago, USA, March 2017. |
| Software | Borchert O., Kim O., Hannachi L., Montgomery D., Sriram K., NIST RPKI Monitor and Test System, NIST test and measurement tool., March 2017. |
| Presentation | Adalier M., Sriram K., Borchert O., Lee K., Montgomery D., High Performance BGP Security: Algorithms and Architectures, North American Network Operators Group Meeting (NANOG-69), Washington D.C., February 2017. |
| Presentation | Borchert O., BGPSec Interoperability Test QuaggaSRx and BIRD BGPsec, IETF97 Conference, Seoul, November 2016. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Enhanced Feasible-Path Unicast Reverse Path Filtering, Presentation to the GROW Working Group, IETF-97, November 2016. |
| Workshop | Montgomery D., Murphy S., Practical BGP Origin Validation using RPKI: Vendor Support, Signing and Validation Services, and Operational Experience, North American Network Operators Group (NANOG 67), Chicago IL, June 2016. |
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Montgomery D., McPherson D., Osterweil E., Dickson B., Problem Definition and Classification of BGP Route Leaks, Internet Engineering Task Force, RFC7908, June 2016.
|
| Standards Specification | Manderson T., Sriram K., White R., Use Cases and Interpretations of Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) Objects for Issuers and Relying Parties, Internet Engineering Task Force, RFC6907, October 2015. |
| Standards Specification | Sriram K., Kumari W., Recommendation for Not Using AS_SET and AS_CONFED_SET in BGP, Internet Engineering Task Force, RFC6472, October 2015. |
| Software | Spies S., Borchert O., NIST BGPSec / RPKI Interoperability Test and Evaluation (BRITE) System, NIST developed online test tool and test scripts for BGP RPKI origin validation testing., May 2015. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Bush R., RIB Size and CPU Workload Estimation for BGPSEC, Presentation at the IETF-91 Joint IDR/SIDR WG Meeting, November 2014. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Enhancement to BGPSEC for Detection/Mitigation against Route Leaks, Presentation at the IETF-90, GROW WG Meeting, July 2014. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Bush R., Estimating CPU Cost of BGPSEC on a Router, Presented at IETF-83 SIDR WG Meeting, March 2013. |
| Standards Contribution | Kent S., Sriram K., RPKI Rsync Download Delay Modeling, Presented at the IETF-86, SIDR WG Meeting, March 2013. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Borchert O., Kim O., Gleichmann P., Montgomery D., Routing Data Quality and Its Impact on BGP Anomaly Detection Algorithms, ISOC Routing Resiliency Measurements Workshop, Atlanta, November 2012. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Realistic Model of the Load Due to BGPSEC Beacons, Presented at IETF SIDR WG Interim meeting, San Diego, February 2012. |
| Presentation | Borchert O., Spies S., Lee K., Montgomery D., Sriram K., Kim O., NIST BGP-SRx (BGPSecure Router eXtension) and BRITE (BGPSEC/RPKI Interoperability Test and Experimentation), Presented at NANOG 53, Philadelphia, October 2011. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram K., Borchert O., Kim O., Cooper D., Montgomery D., RIB Size Estimation for BGPSEC, Presented at the IETF-81, SIDR WG Meeting, July 2011. |
| Presentation | Kim O., Sriram K., Borchert O., Montgomery D., Characterization of the Size and Shape of Static RPKI, NIST presentation (draft), December 2010. |
| Conference Publication | Sriram K., Gleichmann P., Kim Y.T., Montgomery D., Enhanced Efficiency of Mapping Distribution Protocols in Scalable Routing and Addressing Architectures, Proceedings of the IEEE ICCCN 2010, Zurich, August 2010. |
| Standards Contribution | Sriram O. Borchert K., Kim O., Gleichmann P., Montgomery D., Measurement Data on AS_SET and AGGREGATOR {Prefix, Origin} Validation Algorithm, Presented at the IETF-78, SIDR WG Meeting, July 2010. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Gleichmann P., Kim Y.T., Montgomery D., Enhanced Efficiency of Mapping Distribution Protocols in Scalable Routing and Addressing Architectures, Presentation to the LISP WG meeting at the 78th IETF, July 2010. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Borchert O., Kim O., Gleichmann P., Potential Impact of BGPSEC Mechanisms on Global BGP Dynamics, Presentation to BGPSEC Design Team, October 2009. |
| Presentation | Kim O., Sriram K., Borchert O., Gleichmann P., Montgomery D., An Analysis of ARIN NetHandles with OriginAS Data and Analysis of RIR/IRR Registry Data, Presented at ARIN XXIII, San Antonio, TX, April 2009. |
| Conference Publication | Sriram K., Borchert O., Kim O., Gleichmann P., Montgomery D., A Comparative Analysis of BGP Anomaly Detection and Robustness Algorithms, Cybersecurity Applications & Technology Conference for Homeland Security (CATCH)), Washington, DC, USA, 2009, pp. 25-38, doi: 10.1109/CATCH.2009.20, March 2009. |
| Presentation | Borchert O., Kim O., Sriram K., Montgomery D., TERRAIN: Testing and Evaluation of Routing Robustness in Assurable Inter-domain Networking, Presentation at the Cybersecurity Applications and Technology Conference for Homeland Security (CATCH), Washington D.C., March 2009. |
| Presentation | Sriram K., Borchert O., Kim O., Gleichmann P., Montgomery D., Evaluation of BGP Anomaly Detection and Robustness Algorithms, Presented at NANOG-43, June 2008. |
| NIST Publication | Kuhn D.R., Sriram K., Montgomery D., Border Gateway Protocol Security, NIST Special Publication 800-54, Obsoleted by NIST SP-800-189, July 2007. |
| Journal Publication | Sriram K., Montgomery D., Borchert O., Kim O., Kuhn D.R., Study of BGP Peering Session Attacks and Their Impacts on Routing Performance, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications: Special issue on High-Speed Network Security, Vol. 24, No. 10, pp. 1901-1915, doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2006.877218, October 2006. |
| Journal Publication | Montgomery D., Murphy S., Toward Secure Routing Infrastructures, Security &, Privacy, IEEE, vol.4, no.5, pp.84,87, September 2006. |
Collaborators (68) = APNIC, ARIN, AT&T, Akamai, Akamai Technologies, Antara Teknik LLC, Arrcus, BBN Technologies, Boston University, CableLabs, Charter Communications, Cisco, Cloudflare, Columbia University, Comcast, Czech NIC, DE CIX, Fastley, Fastly, Federal Communications Commission, George Washington University, Georgia Tech University, GoDaddy, Google, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Huawei, IIJ, ISOC, Internet Initiative Japan, Internet Initiative Japan (IIJ), Internet Neutral Exchange Association (INEX), Internet Society, Internet2, Juniper, Juniper Networks, Kentik, Lumen, MIT, NCTA, NIST, NLnet Labs, NTIA, NTT, National Science Foundation, Netscout, New College of Florida, None, OpenBGPD Org., Parsons, Princeton University, Qrator Labs, RIPE NCC, Research institute CODE, SkyUK, Tsinghua University, Universitaet der Bundeswehr Muenchen, University of Chicago, University of Connecticut, University of Kentucky, University of Twente, Verisign, W3C/MIT, Workonline Communications, Yandex, ZDNS, Zhongguancun Laborator, Zhongguancun Laboratory, sn3rd

