Liquid Volume Calibration Facility
Summary
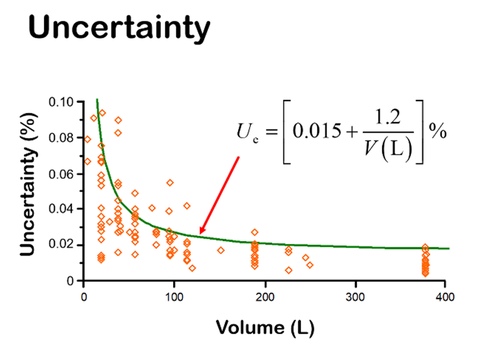
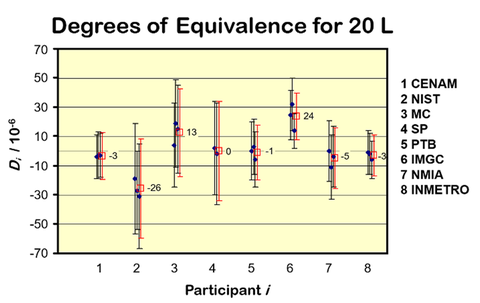
The United States consumes approximately 1,200 metric tons of petroleum annually, which equates to 11 liters per person per day. Half of this petroleum is imported from other countries. Within the U.S., the majority of petroleum (two-thirds) is transported through pipelines, the most cost-effective and efficient method for distribution across the country. NIST calibrates the interior volume of test measurers ranging from 1 liter to 1,900 liters to provide SI traceability for petroleum custody transfer. The uncertainty in the calibration ranges between 0.1 % and 0.02 % of the volume and is given by Figure 1. The calibrated volume of these test measures is used to calibrate flow meters involved in the buying and selling of trillions of dollars' worth of petroleum. NIST’s facility uses reverse osmosis, deionized water for calibration and applies gravimetric and volumetric methods to determine volume. Each calibration is assigned a unique uncertainty value to ensure precision and compliance with industry standards. NIST participates in key comparisons with other National Metrology Institutes, achieving results within a 0.0025% margin, Fig. 2.
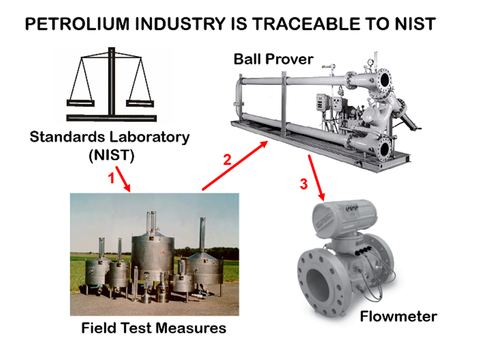
The test measures NIST calibrates are used by water draw companies to calibrate essential equipment, including tanks, ball provers, and stationary tanks, all of which are vital for ensuring accurate volume measurement during custody transfer in the petroleum industry. Figure 3 illustrates the calibration cycle, showing how low-uncertainty measurements at NIST directly impact the flow meters used in the buying and selling of petroleum.
Description
The NIST liquid volume calibration service offers calibration services for volumes ranging from 1 liter to 1,900 liters in a temperature-controlled environment. For volumes up to 377 liters, NIST uses the gravimetric method, while volumes between 378 and 1,900 liters are calibrated using the volume transfer method. The gravimetric method uses reverse osmosis (RO), deionized water, a weigh scale, and the known density the water to determine the internal volume of a test measure. The volume transfer method uses pipettes whose volume was determined via the gravimetric method to transfer water to the test measure, thereby determining its volume.
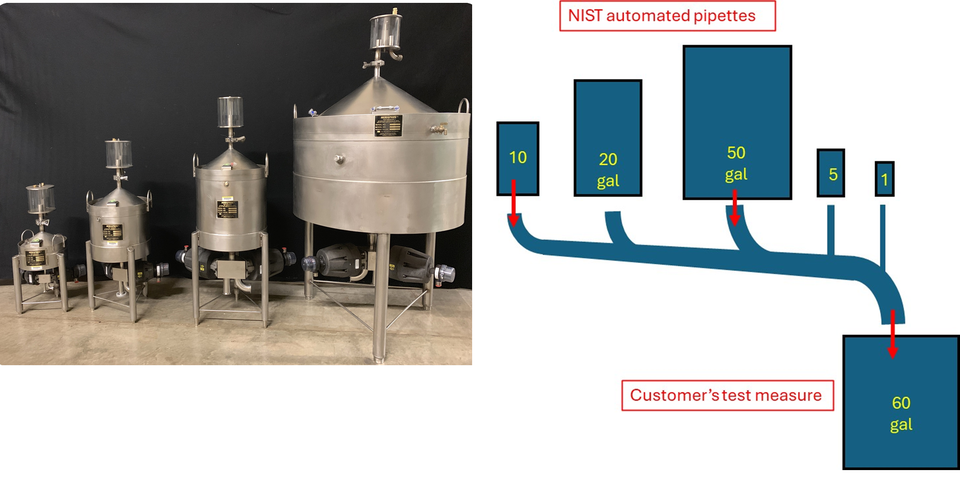
Currently, NIST is undergoing a major renovation of its volume laboratory, with completion expected in about one year. This renovation will help reduce customer wait times for calibrations, further enhancing service efficiency.

