A Walk Through Time - Early Clocks
Not until somewhat recently (that is, in terms of human history) did people find a need for knowing the time of day. As best we know, 5000 to 6000 years ago great civilizations in the Middle East and North Africa began to make clocks to augment their calendars. With their attendant bureaucracies, formal religions, and other burgeoning societal activities, these cultures apparently found a need to organize their time more efficiently.
 Sun Clocks
Sun Clocks

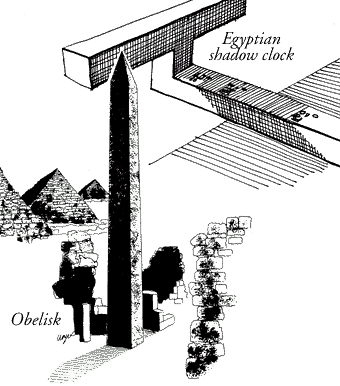
The Sumerian culture was lost without passing on its knowledge, but the Egyptians were apparently the next to formally divide their day into parts something like our hours. Obelisks (slender, tapering, four-sided monuments) were built as early as 3500 BCE. Their moving shadows formed a kind of sundial, enabling people to partition the day into morning and afternoon. Obelisks also showed the year's longest and shortest days when the shadow at noon was the shortest or longest of the year. Later, additional markers around the base of the monument would indicate further subdivisions of time.
Another Egyptian shadow clock or sundial, possibly the first portable timepiece, came into use around 1500 BCE. This device divided a sunlit day into 10 parts plus two "twilight hours" in the morning and evening. When the long stem with 5 variably spaced marks was oriented east and west in the morning, an elevated crossbar on the east end cast a moving shadow over the marks. At noon, the device was turned in the opposite direction to measure the afternoon "hours."
The merkhet, the oldest known astronomical tool, was an Egyptian development of around 600 BCE. A pair of merkhets was used to establish a north-south line (or meridian) by aligning them with the Pole Star. They could then be used to mark off nighttime hours by determining when certain other stars crossed the meridian.
In the quest for better year-round accuracy, sundials evolved from flat horizontal or vertical plates to more elaborate forms. One version was the hemispherical dial, a bowl-shaped depression cut into a block of stone, carrying a central vertical gnomon (pointer) and scribed with sets of hour lines for different seasons. The hemicycle, said to have been invented about 300 BCE, removed the useless half of the hemisphere to give an appearance of a half-bowl cut into the edge of a squared block. By 30 BCE, Vitruvius could describe 13 different sundial styles in use in Greece, Asia Minor, and Italy.
 Elements of a Clock
Elements of a Clock

Before we continue describing the evolution of ways to mark the passage of time, perhaps we should broadly define what constitutes a clock. All clocks must have two basic components:
- a regular, constant or repetitive process or action to mark off equal increments of time. Early examples of such processes included the movement of the sun across the sky, candles marked in increments, oil lamps with marked reservoirs, sand glasses (hourglasses), and in the Orient, knotted cords and small stone or metal mazes filled with incense that would burn at a certain pace. Modern clocks use a balance wheel, pendulum, vibrating crystal, or electromagnetic waves associated with the internal workings of atoms as their regulators.
- a means of keeping track of the increments of time and displaying the result. Our ways of keeping track of the passage of time include the position of clock hands and digital time displays.
The history of timekeeping is the story of the search for ever more consistent actions or processes to regulate the rate of a clock.
Water Clocks
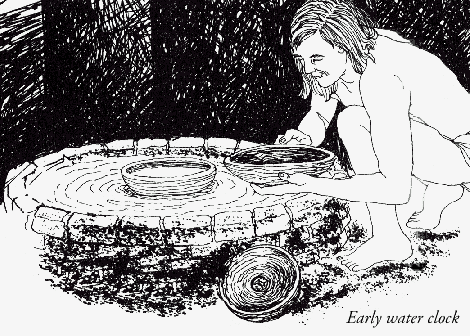
Water clocks were among the earliest timekeepers that didn't depend on the observation of celestial bodies. One of the oldest was found in the tomb of the Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep I, buried around 1500 BCE. Later named clepsydras ("water thieves") by the Greeks, who began using them about 325 BCE, these were stone vessels with sloping sides that allowed water to drip at a nearly constant rate from a small hole near the bottom. Other clepsydras were cylindrical or bowl-shaped containers designed to slowly fill with water coming in at a constant rate. Markings on the inside surfaces measured the passage of "hours" as the water level reached them. These clocks were used to determine hours at night, but may have been used in daylight as well. Another version consisted of a metal bowl with a hole in the bottom; when placed in a container of water the bowl would fill and sink in a certain time. These were still in use in North Africa in the 20th century.
A Macedonian astronomer, Andronikos, supervised the construction of his Horologion, known today as the Tower of the Winds, in the Athens marketplace in the first half of the first century BCE. This octagonal structure showed scholars and shoppers both sundials and mechanical hour indicators. It featured a 24 hour mechanized clepsydra and indicators for the eight winds from which the tower got its name, and it displayed the seasons of the year and astrological dates and periods. The Romans also developed mechanized clepsydras, though their complexity accomplished little improvement over simpler methods for determining the passage of time.
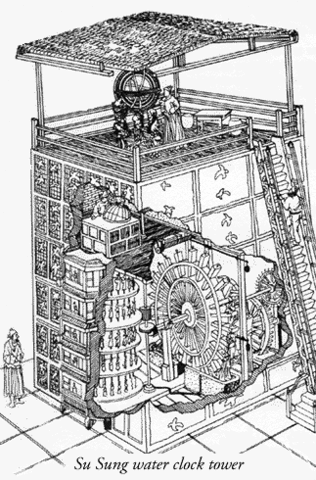
In the Far East, mechanized astronomical/astrological clock making developed from 200 to 1300 CE. Third-century Chinese clepsydras drove various mechanisms that illustrated astronomical phenomena. One of the most elaborate clock towers was built by Su Sung and his associates in 1088 CE. Su Sung's mechanism incorporated a water-driven escapement invented about 725 CE. The Su Sung clock tower, over 30 feet tall, possessed a bronze power-driven armillary sphere for observations, an automatically rotating celestial globe, and five front panels with doors that permitted the viewing of changing manikins which rang bells or gongs, and held tablets indicating the hour or other special times of the day.
Since the rate of flow of water is very difficult to control accurately, a clock based on that flow could never achieve excellent accuracy. People were naturally led to other approaches.
Notice of Online Archive: This page is no longer being updated and remains online for informational and historical purposes only. The information is accurate as of 2004. For questions about page contents, please pml-webmaster [at] nist.gov (subject: A%20Walk%20Through%20Time) (contact us).

