NIST 5G Open-Source Testbed Automation Tool

Based on the blueprints described in NIST TN 2311, this automation tool facilitates the deployment and configuration of 5G Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) testbeds. Designed to operate in both bare metal and virtualized environments, it simplifies setting up the components required for a 5G O-RAN testbed including the 5G Core, Next Generation Node B (gNodeB), User Equipment (UE), RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC), and a series of xApps that can be installed in the RIC. This reduces the complexity and time required to operationalize the testbeds described in the report above and enables more efficient testing and validation to facilitate research and development in 5G technologies.
- All software described on this page is covered by the NIST software disclaimer.
- Questions or comments can be sent to itrg-contact [at] list.nist.gov (itrg-contact[at]list[dot]nist[dot]gov).
Uses
The automation tool is designed to support diverse software components for 5G O-RAN testbeds. It provides a framework for deploying and configuring these components, allowing users to quickly set up and test different configurations. The automation scripts are primarily written in Linux shell, C/C++, and Python, and are designed to be modular and extensible. This allows users to configure the components to meet specific requirements, and add components as needed.
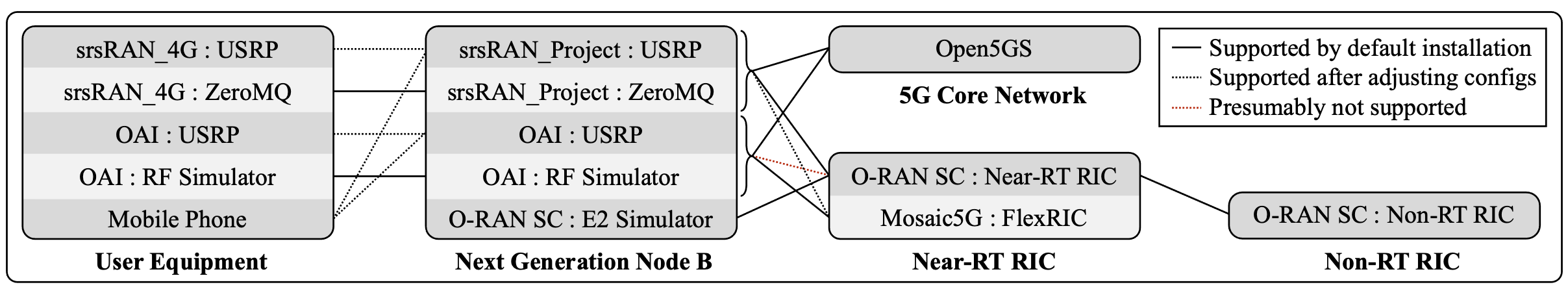
Below is a list of the software components that are supported by this automation tool. The list may change over time as new components are added or existing components are updated. The software components are grouped by their function in the 5G O-RAN testbed.

Additionally, the diagram below illustrates the connectivity between the components that have been experimentally verified. The components are grouped by their function in the 5G O-RAN testbed. The lines connecting the components indicate the communication paths between them. A solid line indicates a default configuration, a dashed line indicates a configuration that requires additional configuration changes to be operational, and a dashed red line indicates a configuration not yet supported in the default tool, but which is under active or planned development.
- Certain equipment, instruments, software, or materials are identified on this site in order to specify the experimental procedures adequately. Such identification is not intended to imply recommendation or endorsement of any product or service by NIST, nor is it intended to imply that the materials or equipment identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.
Related Publications
Contact
Questions or comments can be sent to itrg-contact@list.nist.gov.
-
(301) 975-3249

