SimPROCESD
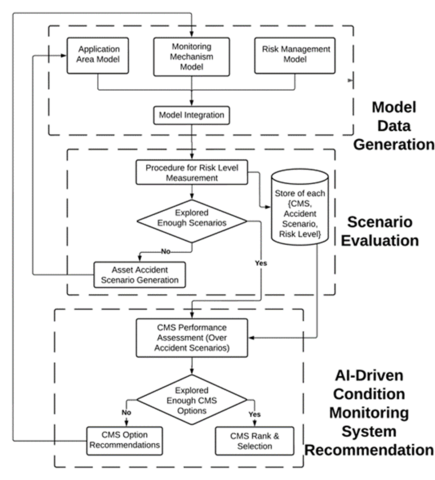
Sim-PROCESD can be used to evaluate and compare condition monitoring systems along side various control or maintenance policies
SimPROCESD (or Simulated-Production Resource for Operations & Conditions Evaluations to Support Decision-making) is a discrete-event simulation package written in Python that is designed to model the behavior of discrete manufacturing systems. Specifically, it focuses on asynchronous production lines with finite buffers. It also provides functionality for modeling the degradation and maintenance of machines in these systems.
In addition to modeling the behavior of existing systems, SimPROCESD is also intended to help with optimizing those systems by simulating various changes to them and reviewing the results. For instance, users may be interested in evaluating alternative maintenance policies for a particular system.
The software is available for public use through a publicly available GitHub repository. Any user may create a fork (copy) of the repository to freely experiment (e.g., class extensions to model complex processes) with the code without affecting the original source code.
NOTE: SimPROCESD project is in early development and may receive updates that are not backwards compatible.
Current published version:
Github - https://github.com/usnistgov/simprocesd/blob/master/setup.py
PyPi - https://pypi.org/project/simprocesd/
Our user guide, including API, is available at:
https://usnistgov.github.io/simprocesd/
Uses
SimPROCESD is designed to be a flexible, open source tool to support a broad range of analysis and planning for process manufacturing.
The major elements allow for production planning, maintenance policy evaluation, and condition monitoring systems evaluation.
Indicators such as part quality, equipment health, resource use, and others can be tracked and gauged in any arbitrary metric or KPI relevant to the user.
Tracking many standard metrics, such as net production profit, or part quality are demonstrated in our Examples Page:
https://usnistgov.github.io/simprocesd/examples.html
Relevant Publications:
- Dadfarnia, Mehdi, Michael E. Sharp, Serghei Drozdov, and Jeffrey W. Herrmann. "A Simulation-Based Approach to Assess Condition Monitoring-Enabled Maintenance in Manufacturing." In 2023 7th International Conference on System Reliability and Safety (ICSRS), pp. 413-422. IEEE, 2023.
- Dadfarnia, Mehdi, and Michael Sharp. "Key elements to contextualize ai-driven condition monitoring systems towards their risk-based evaluation." In 2022 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Industries (AI4I), pp. 38-41. IEEE, 2022.
- Sharp, Michael, Mehdi Dadfarnia, Timothy Sprock, and Douglas Thomas. "Procedural guide for system-level impact evaluation of industrial artificial intelligence-driven technologies: Application to risk-based investment analysis for condition monitoring systems in manufacturing." Journal of manufacturing science and engineering 144, no. 7 (2022): 071008.
- Dadfarnia, Mehdi, Michael Sharp, and Timothy Sprock. "Understanding and evaluating naive diagnostics algorithms applicable in multistage manufacturing from a risk management perspective." In International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, vol. 84263, p. V002T07A042. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020.
Contact
-
(301) 975-4251
-
(301) 975-0476

