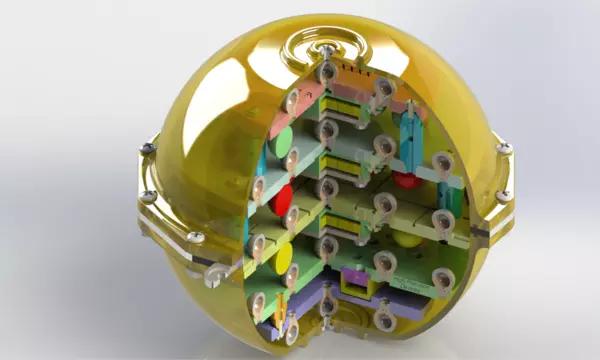
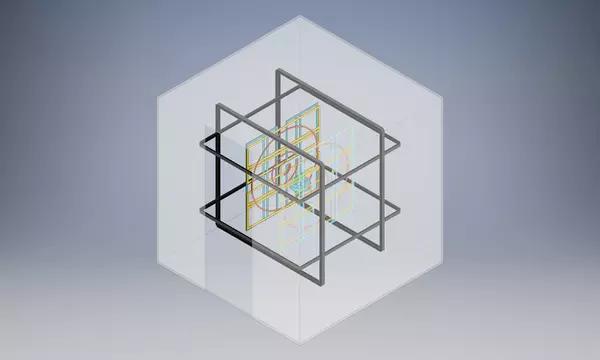
News and Updates
Publications
Awards
Press Coverage
TAKING MEASURE BLOG
Contacts
Group Leader
-
(303) 497-4657