Problem
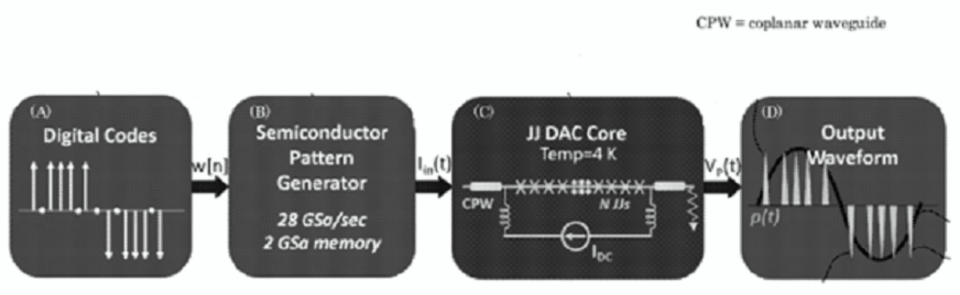
There is a need for a pulse quantizer that uses arrays of one or more Josephson junctions to create a pulse voltage output that is immune to differential pulse timing shifts.
Invention
We have invented a pulse quantizer that uses arrays of one or more Josephson junctions to create a pulse voltage output that is immune to differential pulse timing shifts. When the output pulse patterns are used to encode a waveform, for example, the waveform will be free from pulse timing shifts that degrade the accuracy and signal purity of the synthesized waveform.
Potential Commercial Applications
Quantum-accurate voltage waveform synthesis for AC voltage metrology and programmable arbitrary waveform synthesizers for RF applications, especially for megahertz and gigahertz calibration sources for LTE and 5G communications.
Drivers for bias and controlling other circuits and devices, such as pulse bias control and characterization of qubits or data input applied to superconducting or other advanced computers (e.g., digital, quantum, reversible, or neuromorphic processors).
Calibration of AC voltage at frequencies up to a few megahertz is currently used in AC voltage calibration systems and in research applications. There are none that are commercially available. This invention has the potential to extend the frequency range, signal purity, and accuracy of synthesized waveforms to frequencies of tens or hundreds of gigahertz.
Competitive Advantage
Only instrument available as a quantum-accurate voltage source that eliminates the differential pulse timing error in the presence of unknown leakage or nonzero bias currents.

