Optical Aperture Area and Coordinate Measurement Facility
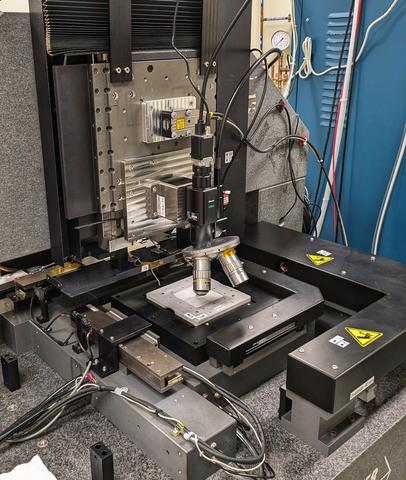
NIST has established an absolute aperture area measurement facility primarily intended for area calibrations of defining apertures used in radiometric instruments, that are traceable to the International System of Units (SI) length unit.
The aperture area measurement (AAM) instrument is a specialized planar coordinate measuring machine (CMM) that combines a precision XY air bearing stage with transmitted or reflected light microscopy. The AAM instrument is built on a dimensionally stable granite structure that provides a flat base for the air bearings, and a granite arch to hold the microscope on a vertical linear stage. The movement of the horizontal stage’s X and Y axes are controlled by laser interferometers, which directly link the stage position to the SI meter through the wavelengths of the helium-neon laser near 632.8 nm. The errors of the combined X and Y stages are calibrated with a NIST SRM-5001 grid standard that is itself traceable to the SI length unit. The workspace of the horizontal stage system is approximately 100 mm by 100 mm.
The microscope is a brightfield microscope that can be operated in transmitted and reflected light modes. The optical distortion of the microscope is characterized by moving a fiducial mark through the microscope’s field of view using the calibrated horizontal motion stage. With this calibration method the lateral resolution and image distortion can be determined for the full field of view of the microscope objectives and the positions of the image pixels can be mapped into the coordinate system of the horizontal motion stages.
Radiometric apertures are always measured with transmitted light as they would be used in their applications. A narrow-bandwidth LED (light emitting diode) illuminator with a wavelength of 525 nm illuminates an aperture through an opening in the granite base at the center of the horizontal stage. The light diffracted at the aperture edge is imaged by the microscope on an image sensor using a microscope objective with high numerical aperture. This allows the aperture edge to be located accurately in the coordinate system of the motion stage. In a typical aperture area calibration, the edge of an aperture is imaged at about 180 locations and from each image the positions of between 1000 and 2000 edge pixels are determined. The aperture area is then calculated from the positions of all edge pixels in the stage coordinate system.
When operated in reflected light mode, a broad-band LED illuminator is used to illuminate a part under test through the microscope objective. This mode is suitable e.g., for the calibration of optical grid calibration targets or similar calibration targets for the performance characterization of optical imaging systems.
Specifications/Capabilities
The AAM instrument can measure apertures with shapes ranging from circular to rectangular (slits). Circular apertures with diameters from 0.5 mm to 50 mm are measured routinely. Grid standards and similar dimensional standards can be calibrated provided they fit within the workspace of the instrument. Additional details of the measurement procedures can be found in the description of aperture area measurements.

