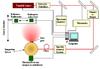
The group’s mission is to realize the NIST detector-based radiometry scale through cryogenic electrical substitution radiometers and disseminate this scale via sensor responsivity calibrations to radiant power, irradiance, and/or radiance for customers seeking the highest accuracy possible. Sensors calibrated against the Primary Optical Watt Radiometer (POWR), which resides within the SIRCUS laboratory, are the basis of the NIST realization of the SI unit of the Candela and serve as reference radiometers at SIRCUS and other facilities at NIST. SIRCUS in turn serves as the basis for the NIST irradiance scale that calibrates FEL irradiance lamps and provides calibration for radiometers that serve the remote sensing community and others. The LBIR facility provides calibrations of blackbody and other sources and detectors that operate in a low-background infrared environment, typically in space-simulating vacuum chambers in which cryogenically-cooled interior shrouds surround the instruments. The group also establishes and disseminates measurement scales for infrared properties of materials and performs supporting theoretical analysis.
CALIBRATION SERVICES AND STANDARD REFERENCE MATERIALS
COLLABORATION OPPORTUNITIES
The Remote Sensing Group welcomes opportunities to collaborate on joint research, technology, and standards development projects to advance the characterization and calibration of remote sensing technology. The group provides multiple opportunities for students, scientists, industry, academia, and other R&D laboratories to collaborate. Specific opportunities depend on current areas of interest within the Group, but may include undergraduate research fellowship, postdoctoral fellowships, visiting scientist, and guest researchers as well as various cooperative research arrangements ranging from formal agreements, such as CRADA, Consortia, and interagency agreements, to informal collaborations. For more details, see Employment and Internship Opportunities and Collaboration Opportunities and the NRC post-doc site.
News and Updates
Awards
Software
Contacts
Group Leader
-
(301) 975-2133