Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) Program: Standards, Services, and Training
Summary
The NIST Office of Weights and Measures (OWM) and the Physical Measurement Laboratory (PML) have developed an Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) Program comprised of legal metrology standards and electrical metrology-based measurement services to support the U.S. state weights and measures authorities responsible for testing and official inspections of EV charging infrastructure. Our work supports the verification of operational requirements for commercially supplied EV chargers thereby ensuring that consumers get what they pay for and EV charging industry suppliers get fair payment for their services. In addition to supporting marketplace equity, these standards and measurement services underpin U.S. economic competitiveness and fair trade in this critical and emerging technology area.
The Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) Program includes:
- Documentary standards and guidance documents related to EVSE technical specifications
- SI traceable DC electric power and energy calibrations, transfer meter measurement services, and interlaboratory studies to improve the accuracy and comparability of measurements
- Metrology-based EVSE training curriculum for state regulatory officials and other industry stakeholders
Description

Weights and measures authorities in each U.S. state and local jurisdiction are responsible for the testing and official inspection of electric vehicle (EV) chargers, specifically the measurement devices that deliver electricity as fuel within commercial EV chargers. These devices are commonly referred to as Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) and are commercially available in a range of types, including the more popular "fast" or direct current (DC) EV chargers.
EVSEs can be considered similar to retail motor fuel dispensers (aka gas pumps) in how they should deliver fuel to vehicles with respect to the applicable weights and measures specifications, tolerances, and other technical requirements (i.e., code within NIST Handbook 44). Specifically, these legal metrology-controlled devices are to provide accurate and repeatable fuel delivery while facilitating clear and transparent transactions for both buyer and seller and preventing fraud.
OWM and its PML partners have developed an EVSE Program consisting of documentary standards, measurement services, and metrology-based training to underpin a technically sound and uniform nationwide EV charging infrastructure that supports marketplace equity.
1. Documentary Standards and Technical Guidance for EVSE Inspections
OWM has a unique role in working with state officials and governments, other federal agencies, and industry and manufacturing stakeholders to develop, refine, and publish standardized model EV fueling laws and regulations. This is achieved through OWM's technical guidance within a U.S. National Working Group on Electric Vehicle Fueling and Submetering and the National Council on Weights and Measures (NCWM) standards development process. These standards development activities leverage our OWM Technical Analysis of NCWM committee agenda items, including EV fueling. This has resulted in two documentary standards as NIST Handbooks that describe the technical specification, tolerances, and overall performance of EV supply equipment (EVSE):
- NIST Handbook 44 Section 3.40 Electric Vehicle Fueling Systems
- NIST Handbook 130 Section III. Uniform Regulation for the Method of Sale of Commodities
These NIST Handbooks serve as U.S. weights and measures standards. They are updated annually following the endorsement of amendments by the NCWM during its Annual meeting. They also serve as current model laws and regulations for state adoption.
Visit our Electric Vehicle Fueling FAQs to learn more about EVSE documentary standards and the technical specifications.
State weights and measures regulatory officials (i.e., inspectors) then utilize the technical specifications in NIST Handbooks 44 and 130 to test and verify that commercial EV chargers meet operational requirements. OWM also provides an Examination Procedure Outline (30) for Retail Electric Vehicle Fueling Systems that serves as the basis for field testing by inspectors based on NIST Handbook 44 content. Similar to the routine inspection of retail motor fuel dispensers (i.e. gas pumps), a regular and uniform approach to EVSE inspections across all state and local jurisdictions will ensure marketplace equity in commercial EV charging transactions.

To learn more about the policies and rules for commercial EV fueling across the U.S. (published in September 2023), see our NIST Special Publication:
NIST SP 2200-03 An Evolving Regulatory Landscape for Commercial Electric Vehicle Fueling.
2. DC Power and Energy Calibration and Measurement Services
OWM is also partnering with the Applied Electrical Metrology group in PML (PML-AEM) to evaluate commercial off-the-shelf instruments or meters that NIST will be able to calibrate, instruments that can, in turn, be used to calibrate DC-based EVSEs in the field. These intermediary instruments, or DC Transfer Reference Meters (TRMs) are expected to be used by state metrology and secondary testing laboratories to transfer the calibration traceability to EVSEs. Calibration procedures will also be developed and used to test field-installed EVSEs for accuracy. These TRMs will ultimately connect to a primary DC standard via a NIST Calibration Service and provide traceability for EVSE applications of DC electric power and energy measurements to SI-based standards of voltage, resistance (for current), and time.
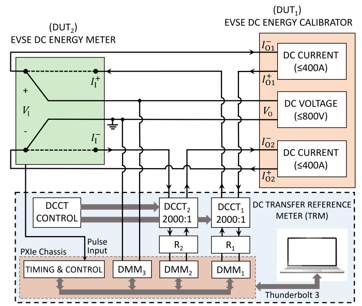
To realize SI traceability and validate the NIST prototype DC TRM, OWM is facilitating a 2024-2025 international interlaboratory study with PML-AEM and other select National Metrology Institutes (PTB of Germany; METAS of Switzerland, and INMETRO of Brazil). This is the first step to establishing internationally recognized calibration and measurement capabilities for the DC measurement service. The study will ultimately improve the accuracy and comparability of high-power DC measurements necessary for equitable EV fast charging in the U.S.
OWM is presently developing a technical guidance document (NIST SP 2200 series) that will detail methods for establishing traceability to primary SI standards in the measurement of DC electrical quantities for EVSE test instrumentation. This will include a description of the equipment and procedures and outline methods used by the available test instrumentation to evaluate EVSEs. A description of the general procedures will include a statistical analysis of the measurements to provide an estimated uncertainty in the measurement. This document will be intended for manufacturers of field test standards as well as owners and users of this equipment, including state metrology laboratories, state weights and measures authorities, registered installation service providers, manufacturers of EVSEs, and other stakeholders.
The anticipated publication of this NIST SP 2200 is in early 2025.
For more details, visit the background on the NIST activities page for providing calibration and, ultimately, SI traceability to EV charging infrastructure.
3. EVSE Metrology Training
OWM is developing a new 2025 EVSE metrology training curriculum aimed at state weights and measures officials and other EVSE industry stakeholders. This training will be foundational to ensuring equity in the EV charging market by giving trainees the expertise to evaluate EVSEs for compliance with commercial standards developed by state regulators and members of the U.S. EVSE industry. The intended audience for training includes weights and measures officials, Registered Service Agents (RSAs), EVSE engineers, technicians, manufacturers, and other relevant industry stakeholders.
Building upon OWM's deep experience in metrology training, OWM will develop an in-person 5-day EVSE metrology course that will introduce participants to fundamental concepts and provide a framework of applied electric metrology for EVSE used at commercial EV charging stations. The course will also provide introductory modules on the concepts of measurement systems, good laboratory practices, measurement uncertainty, measurement assurance, traceability, basic statistics, and how they fit into a laboratory Quality Management System.
The curriculum will also include laboratory and field-based demonstrations and hands-on practical sessions for EVSE assessment and performance according to specifications and tolerances in NIST Handbook 44 and international standards (e.g., OIML Guide 22) as appropriate. Topics will be covered using a variety of laboratory measurements, case studies, and field conditions so that the participants will be able to apply the concepts to any EVSE testing/field measuring device upon completion. Topics are covered in a mixture of training styles, including lectures, hands-on exercises, case studies, field-based tests and evaluations, and discussion.
This EVSE metrology training program is anticipated to be available towards the end of 2025.

Learn more about the OWM Training Program here. If you are interested in future EVSE metrology training, please send an email with your contact information to owm [at] nist.gov (owm[at]nist[dot]gov)

