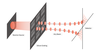
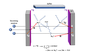
The group is at the forefront of basic research with neutrons. Experiments involve precision measurements of symmetries and parameters of the "weak" nuclear interaction, including measurement of the lifetime of neutrons using thermal and ultra-cold neutron improved cold neutron counting techniques, setting a limit on the time-reversal asymmetry coefficient, and radiative decay of the neutron. The neutron interferometry program provides the world's most accurate measurement of neutron coherent scattering lengths important to materials science research and modeling of the nuclear potentials; during 2007-2008, new interferometry experiments to determine the charge distribution of the neutron, and reciprocal space imaging were carried out. We are developing and promoting the applications of efficient neutron spin filters based on laser-polarized He-3. We are pursuing applications for these filters at the NCNR, the Intense Pulsed Neutron Source at Argonne National Laboratory, and the Los Alamos Neutron Science Center.
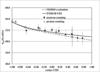
We are enhancing our technical infrastructure to better support neutron standards for national security needs. In addition, we are developing advanced liquid scintillation neutron spectrometry techniques for characterization of neutron fields and for detection of concealed neutron sources with low false-positive rates. We are participating in a Consultative Committee for Ionizing Radiation (CCRI) comparison of thermal neutron fluence rate measurements, characterizing four different beam qualities at the NCNR, and carrying out comparisons of NIST standard neutron sources. We are also leading an effort that will result in a new international evaluation of neutron cross-section standards. We provide two main calibration services: measurement of the emission rate of neutron sources, and calibration of neutron detectors used for personnel protection. Calibrations not falling within these services can be arranged as a special test.
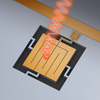
We are applying neutron-imaging methods for industrial research on water transport in fuel cells and on hydrogen distribution in hydrogen storage devices. This facility has provided critical services to major automotive and fuel cell companies during 2007-2010. This is a high demand and high profile nationally recognized program.
In summary, the NI&D group provides measurement services, standards, and fundamental research in support of NIST's mission as it relates to neutron technology and neutron physics. The national interests served include industrial research and development, national defense, homeland security, higher education, electric power production, and, more specifically, neutron imaging, scientific instrument calibration and development, neutron source calibrations, detection of concealed nuclear materials, radiation protection, and nuclear and particle physics data.
News and Updates
Projects and Programs
Publications
Software
Tools and Instruments
Awards
Press Coverage
Contacts
Group Leader
-
(301) 975-8355
Group Secretary
-
(301) 975-6200