Advanced Imaging and Flow Cytometry

BCARS image of a tissue sample
NIST’s strong expertise in optical methods provides the underpinning for a number of measurement assurance and technology development activities in the organization that serve the diagnostics, clinical, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries.
The use of optical technologies in clinical diagnostics and product development often requires certification of instrument performance for regulatory requirements or as part of a quality control process, and reference data, documentary standards, and software tools are essential for instrument performance benchmarking and calibration.
CURRENT ACTIVITIES & PRODUCTS

| Broad Band Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Spectroscopic (BCARS) imaging: Our BCARS program has advanced vibrational spectroscopic imaging to unprecedented levels of sensitivity, making it possible to acquire functional molecular information in living cells. |

| High Resolution Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) imaging: We have demonstrated that SPR imaging, which allows spatially resolved interfacial refractive index changes, can provide spatial resolution that allows the dynamic tracking of cell-secreted proteins and focal adhesions. |

| NIST Flow Cytometry Lab: Our experienced staff leverage the latest cytometry technologies to develop innovative and quantitative flow cytometry measurement solutions, standards, and reference materials to enable quantitative measurements of biological substances |

| Fluorescence Microscopy Benchmarking: We have made available a method to characterize a fluorescence microscope's performance by benchmarking the detection threshold, saturation and linear dynamic range to a physical artifact to help advance this technology from a qualitative to a quantitative method. |

| Absorbance Imaging: A new absorbance imaging method uses a brightfield microscope to make millions of quantitative absorbance measurements using the pixels in the camera array. The method has been applied to maturation of retinal pigment epithelium and trypan blue cell viability measurements. |
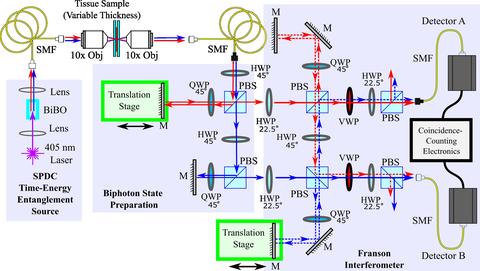
| Quantum Bioimaging and Sensing: Developing tools to take advantage of the quantum nature of light, enabling new biological measurements as well as enhancing existing optical modalities. |
Created April 2, 2016, Updated March 10, 2025

